Introduction :
In Java programming, control flow is crucial for creating efficient and flexible code. The if-else statement is a fundamental control structure that allows you to execute specific blocks of code when certain conditions are met. By understanding if-else in Java, you can build decision-making logic in your programs and improve your coding skills.
What is an if-else Statement?
The if-else statement in Java allows your program to decide which code to run based on whether a condition is true or false.
ifStatement: A block of code is executed if the specified condition istrue.elseStatement: Alternatively, an alternative block of code is run if the condition isfalse.
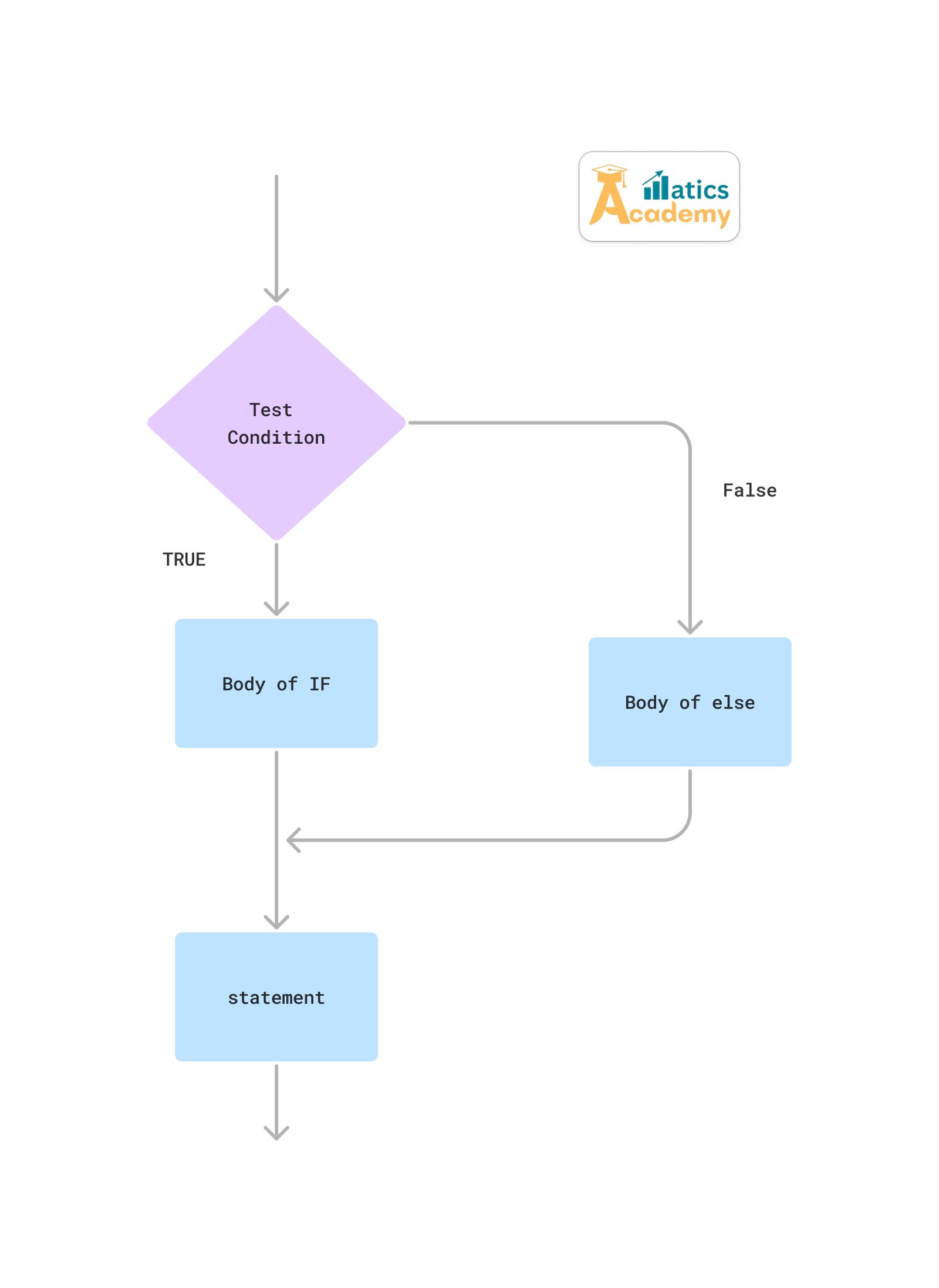
Syntax of if-else in Java
Here, the syntax of an if-else statement in Java is shown
if (condition) {
// Code to execute if the condition is true
} else {
// Code to execute if the condition is false
}How Does the if-else Statement Work?
The workflow of the if-else statement can be broken down into the following steps:
- Condition Evaluation: The program first assesses the condition specified in the
ifclause. - Execution of Code Blocks:If the condition is
true, the code within theifblock is executed. If the condition isfalse, the code in theelseblock is executed instead - Continued Program Flow: After one of the code blocks has been executed, the program continues to the next line of code outside the
if-elsestatement.
Example of if-else in Java
Here, an example is provided to demonstrate how the if-else statement can check if a number is positive or negative:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = -5;
if (number > 0) {
System.out.println("The number is positive.");
} else {
System.out.println("The number is negative or zero.");
}
}
}
Output : The number is negative or zero.
Explanation:
- The condition
(number > 0)checks ifnumberis greater than 0. - If true, “The number is positive.” is printed. Otherwise, “The number is negative or zero.” is displayed.
Common Use Cases
The if-else statement is frequently applied in the following scenarios:
- Validating user input
- Managing program states
- Conditional checks within loops
- Basic error handling
Best Practices for Using if-else Statements
To maximize the effectiveness of if-else statements, these best practices should be followed:
- Keep Conditions Simple: Write clear and straightforward conditions to enhance readability.
- Avoid Deep Nesting: Deeply nested if-else statements can make code harder to follow, so consider using logical operators or
switchstatements if possible. - Use
else iffor Multiple Conditions: If there are more than two conditions, consider usingelse ifto streamline your code.
Key Takeaways
- The
if-elsestatement is essential for decision-making in Java. - Specific blocks of code can be executed based on whether a condition is
trueorfalse. - Additionally, this statement is flexible and can be combined with other control statements for powerful functionality.
Practice Exercise
1.To put this knowledge into action, an if-else statement should be written to check if a number is even or odd and print the result.
2.Create a Java program that takes two integer inputs and prints out the greater number. If the numbers are equal, it should indicate that as well.
3.Write a Java program that checks whether a given year is a leap year or not. A leap year is divisible by 4, but if it’s also divisible by 100, then it must be divisible by 400 to qualify as a leap year.
4.Create a Java program that assigns a grade based on a student’s score. Use the following grading system:
- 90 and above: Grade A
- 80 – 89: Grade B
- 70 – 79: Grade C
- 60 – 69: Grade D
- Below 60: Grade F
5.Write a Java program that checks whether a given number is positive, negative, or zero using an if-else statement.
Advantages of if-else Statements in Java
- Easy Decision-Making: The
if-elsestatement allows you to choose which code to run based on specific conditions. This feature helps your program respond intelligently to different situations. - Clear Code: Using
if-elsestatements makes your code easier to read and understand. This clarity helps both you and other developers quickly grasp the logic behind your decisions. - Error Handling: You can use
if-elsestatements to check for mistakes or invalid inputs. By doing this, you ensure that your program can handle errors smoothly. - Nested Conditions: You can nest
if-elsestatements inside one another, allowing you to create complex decision-making processes. This flexibility helps you manage multiple levels of conditions. - Flexible Control Flow: The
if-elsestatement works well with other control structures, like loops and switch statements. This compatibility gives you various options for managing the flow of your Java programs.
Disadvantages of if-else Statements in Java
- Deep Nesting Problems: If you nest too many
if-elsestatements, your code can become confusing and difficult to follow. This complexity increases the risk of making mistakes. - Performance Issues: When you use many
if-elsestatements, they can slow down your program, especially if the code checks conditions frequently. - Boolean Limitations: The
if-elsestatement primarily handles true/false conditions. For more complex checks, you might need additional logic or different programming methods. - Less Efficient with Multiple Checks: When checking many conditions, using
if-elsecan be less efficient than using aswitchstatement. This is especially true if you check the same variable multiple times. - Alternative Options: Sometimes, other structures, such as
switchstatements or object-oriented programming techniques, offer better solutions than relying solely onif-else.
Interview questions:
1.Explain the if-else statement in Java, and how it differs from a switch statement. (google,amazon,microsoft)
The if-else statement in Java evaluates conditions and executes code based on whether the conditions are true or false. An if block runs when the condition is true, and an else block runs when the condition is false. A switch statement, by contrast, selects code to execute based on the value of a single expression, like an integer, character, or string, making it more efficient for checking multiple, specific values of a single variable
2.How would you handle multiple conditions using if-else statements without making the code overly complex or deeply nested? (microsoft)
Use logical operators (&&, ||) to combine conditions within a single if block. Refactor with else-if for scenarios with three or more conditions. Use helper methods to handle complex logic in a single statement, making the code more readable. When possible, use a switch statement, which can often reduce complexity if checking a single variable against multiple values.
3.Write a code snippet to check if a number is prime using the if-else statement ? (TCS)
public class PrimeCheck {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 29;
boolean isPrime = true;
if (num <= 1) {
isPrime = false;
} else {
for (int i = 2; i <= num / 2; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (isPrime) {
System.out.println(num + " is a prime number.");
} else {
System.out.println(num + " is not a prime number.");
}
}
}
Output : 29 is a prime number
4. Describe the difference between if-else and else-if. In which scenarios would you use each? (ZOHO)
The if statement checks a condition and executes code if it’s true; else provides an alternative path if the if condition is false. The else-if statement, however, allows us to check additional conditions if the initial if condition is false, giving more control over multiple possible states. We use else-if when there are more than two conditions to evaluate in sequence, as it helps avoid deep nesting.
5.Write a Java program using if-else to find the largest of three numbers without using the Math.max() method.? (ACCENTURE)
public class LargestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 15, c = 5;
int largest;
if (a >= b && a >= c) {
largest = a;
} else if (b >= a && b >= c) {
largest = b;
} else {
largest = c;
}
System.out.println("The largest number is: " + largest);
}
}
Output : The largest number is: 15
Test Your Knowledge: If-Else in Java Challenge!
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
