Introduction

Why Study Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is a fundamental principle of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java. It allows methods to take on multiple forms, making code more flexible, reusable, and easier to extend. Understanding polymorphism can improve your coding practices and open doors in fields like software development, mobile apps, and game design.
What Will Be Covered?
You’ll learn about method overloading, method overriding, and dynamic method dispatch. This topic also covers practical examples, code snippets, and visual aids to ensure a clear grasp of polymorphism concepts.
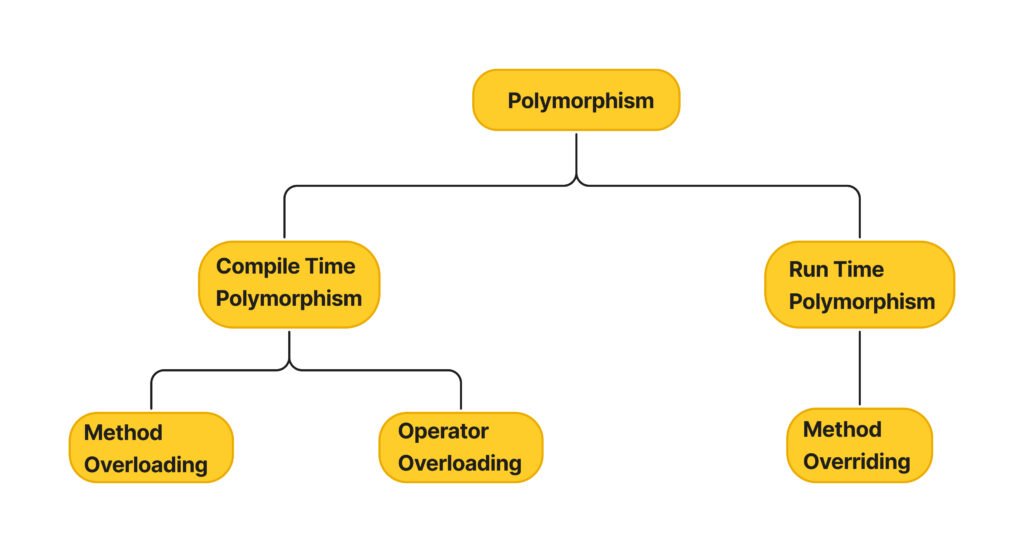
Explanations and Examples
// Superclass
class Animal {
// Method to be overridden
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
// Subclass Dog
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
// Subclass Cat
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Cat meows");
}
}
// Main class
public class PolymorphismExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create Animal object as reference type and assign Dog instance
Animal myDog = new Dog();
myDog.sound(); // Outputs: Dog barks
// Create Animal object as reference type and assign Cat instance
Animal myCat = new Cat();
myCat.sound(); // Outputs: Cat meows
}
}
Explanation
In this program:
- The
Animalclass has a method calledsound. - The
DogandCatclasses inherit fromAnimaland override thesoundmethod to provide specific sounds. - In the
mainmethod, polymorphism allows anAnimalreference to point to either aDogorCatobject. Whensoundis called, Java dynamically selects the correct overridden method based on the actual object type (Dog or Cat).
Polymorphism in Java lets us define one interface with multiple implementations. There are two main types
- Compile-Time Polymorphism (Method Overloading): This happens when multiple methods have the same name but different parameters. Java determines which method to execute at compile time.javaCopy code
class MathOperations { int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } double add(double a, double b) { return a + b; } }
public class Calculator {
// Method to add two integers
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// Overloaded method to add three integers
public int add(int a, int b, int c) {
return a + b + c;
}
// Overloaded method to add two double values
public double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
// Calls the add method with two integer parameters
System.out.println("Sum of two integers: " + calculator.add(10, 20));
// Calls the add method with three integer parameters
System.out.println("Sum of three integers: " + calculator.add(10, 20, 30));
// Calls the add method with two double parameters
System.out.println("Sum of two doubles: " + calculator.add(5.5, 4.3));
}
}
Code Explanation:
Example 1: calculator.add(10, 20)
This calls the method add(int a, int b), which takes two integer parameters. It returns 10 + 20, resulting in 30.
Example 2: calculator.add(10, 20, 30)
This calls the method add(int a, int b, int c), which takes three integer parameters. It returns 10 + 20 + 30, resulting in 60.
Example 3: calculator.add(5.5, 4.3)
This calls the method add(double a, double b), which takes two double parameters. It returns 5.5 + 4.3, resulting in 9.8.
- Runtime Polymorphism (Method Overriding): This occurs when a subclass provides a specific implementation for a method declared in its superclass. Java determines which method to execute at runtime.
// Superclass
class Animal {
// Method to be overridden
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
// Subclass 1
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
// Subclass 2
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Cat meows");
}
}
public class RuntimePolymorphismExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Superclass reference holding subclass objects
Animal myAnimal;
myAnimal = new Dog(); // Dog object
myAnimal.sound(); // Calls Dog's sound method
myAnimal = new Cat(); // Cat object
myAnimal.sound(); // Calls Cat's sound method
}
}
Variable Overshadowing (Hiding)
In Java, when a subclass defines a field (variable) with the same name as in the superclass, it does not override but rather hides the superclass variable. This is known as variable overshadowing or hiding.
Example of Variable Overshadowing
// Superclass
class Parent {
int num = 100; // Parent variable
}
// Subclass
class Child extends Parent {
int num = 200; // This variable overshadows Parent's num
}
// Main class
public class OvershadowingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent obj1 = new Parent();
System.out.println(obj1.num); // Outputs: 100
Child obj2 = new Child();
System.out.println(obj2.num); // Outputs: 200
Parent obj3 = new Child();
System.out.println(obj3.num); // Outputs: 100 (Superclass variable is used)
}
}
🔹 Key Takeaways:
- If you access
numusing aChildobject (obj2.num), it refers to the Child class variable. - If you access
numusing aParentobject (obj1.num), it refers to the Parent class variable. - Even if a Parent reference holds a Child object (
Parent obj3 = new Child();), it will still access the Parent’s variable.
Unlike method overriding, variable overshadowing does not support polymorphism!
Code Explanation:
- Define a superclass
Animalwith a methodsound(). - Create subclasses
DogandCatthat each overridesound()with specific messages. - In the main class, use an
Animalreference to hold different subclass objects (DogandCat), demonstrating polymorphism by callingsound()on each.
Summary
- Polymorphism increases flexibility by allowing one interface with many implementations.
- It simplifies code maintenance, especially in large-scale applications.
Learning Outcomes
- Understand and implement polymorphism with method overloading and overriding.
- Apply polymorphism to create scalable and reusable code in Java applications.
Common Interview Questions
1.What is polymorphism in Java, and why is it important in Object-Oriented Programming?[GOOGLE]
Polymorphism allows multiple implementations under one interface, enhancing flexibility and code reusability.
2.Explain the difference between compile-time and runtime polymorphism.[MICROSOFT]
Compile-time polymorphism is achieved through method overloading, while runtime polymorphism is achieved through method overriding.
3.What is method overloading, and how does it support polymorphism?[AMAZON]
Method overloading allows two or more methods in the same class to have the same name but different parameter lists, allowing flexibility in method selection at compile time.
4.Describe method overriding and how it contributes to runtime polymorphism.[ORACLE]
Method overriding allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation for a method declared in its superclass, enabling dynamic method dispatch at runtime.
5.Can method overloading be considered polymorphism? Why or why not?[TCS]
Yes, method overloading is a form of compile-time polymorphism as the method call is resolved during compilation based on the method signatures.
Practice Exercises
- Create a simple Java program using method overloading to calculate areas of different shapes.
- Implement method overriding in a superclass-subclass structure to show specific animal sounds.
Additional Resources
- Books: “Effective Java” by Joshua Bloch.
- Online Articles: Tutorials on method overloading and overriding.
- Tools: Practice Java coding on platforms like HackerRank or CodeSignal.
- Oracle’s java documentation
Test your Knowledge:
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
