Multithreading in Python allows you to run multiple tasks concurrently, improving the efficiency of your programs. The threading module makes it easy to start and manage threads in Python. In this guide, we will walk you through the process of starting a thread in Python, including basic concepts and practical examples.
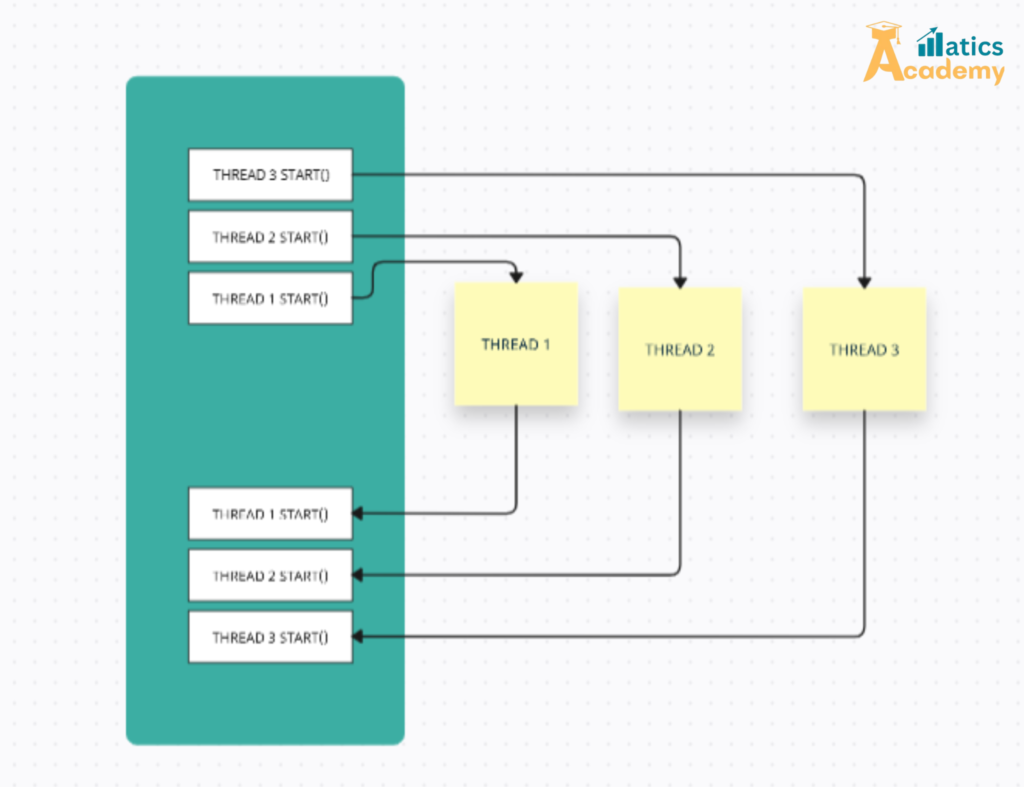
What is a Thread in Python?
A thread is a separate flow of execution within a program. By using threads, you can perform tasks like downloading files, handling user input, or processing data in the background while keeping your main program responsive. Python threads are ideal for I/O-bound tasks that do not require heavy CPU usage.
How to Starting a Thread in Python
To start a thread in Python, you need to use the threading module, which provides a way to create and manage threads. Here’s a simple example to help you get started:
Step 1: Import the threading module
First, you need to import the threading module to work with threads in Python.
import threading
Step 2: Define the task for the thread
Next, define a function that will be executed by the thread. This function will perform the task you want the thread to handle.
def task():
print("Thread is running!")
Step 3: Create a thread
To create a thread, you use the Thread class from the threading module. The target parameter specifies the function that the thread will execute.
# Create a thread to run the task thread = threading.Thread(target=task)
Step 4: Starting a thread
Once the thread is created, you can start it using the start() method. This will initiate the thread and run the task() function.
# Start the thread thread.start()
Step 5: Wait for the thread to finish
To ensure the main program waits for the thread to complete, use the join() method. This makes the main program wait until the thread has finished executing.
# Wait for the thread to finish thread.join()
Complete Example:
import threading
# Define the task that the thread will perform
def task():
print("Thread is running!")
# Create a thread to run the task
thread = threading.Thread(target=task)
# Start the thread
thread.start()
# Wait for the thread to finish
thread.join()
print("Main program finished.")
Why Use Multithreading in Python?
Multithreading is particularly useful when you need to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. For example, it can be used for:
Parallel data processing: Run multiple data processing tasks in parallel without blocking other operations.
Downloading files: While one thread downloads a file, another thread can process data.
Handling user input: One thread can listen for user input while another performs background operations.
Mini Project Code(Starting a Thread) – Checking the thread running
import threading
def task1():
print("Task 1 is running.")
def task2():
print("Task 2 is running.")
def task3():
print("Task 3 is running.")
# Creating threads
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=task1)
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=task2)
thread3 = threading.Thread(target=task3)
# Starting threads
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
thread3.start()
# Main thread continues execution
print("Main thread is still running.")Interview Questions for “Google”
1. What happens when you call the start() method on a thread?
Answer: The start() method begins the execution of the thread by invoking its target function.
2. Can you start a thread multiple times?
Answer: No, a thread can only be started once. Calling start() more than once will raise an error.
3. What is the purpose of the run() method in Python threading?
Answer: The run() method contains the code that the thread will execute when started. It’s automatically called by start().
4. How do threads impact the main program in Python?
Answer: Threads run concurrently with the main program and do not block its execution unless synchronized.
5. What is the difference between start() and run() in threading?
Answer: start() initiates the thread, while run() defines the logic the thread will execute.
Conclusion
Starting a thread in Python is simple and can greatly improve the performance of your programs. By using the threading module, you can handle multiple tasks at once, making your applications more efficient and responsive. Whether you’re working with I/O-bound tasks or just need to run background processes, multithreading is a valuable tool in Python programming.
With this guide, you can now start using threads in your Python programs like creating a thread and starting a thread to enhance their functionality. Happy coding!
