In Python, writing data to a file is one of the essential tasks in file handling. Python provides several ways to write to a file, and the most common method is using the write() function. Here’s a detailed guide on how to write to files in Python, along with some examples.
Writing to a File in Python
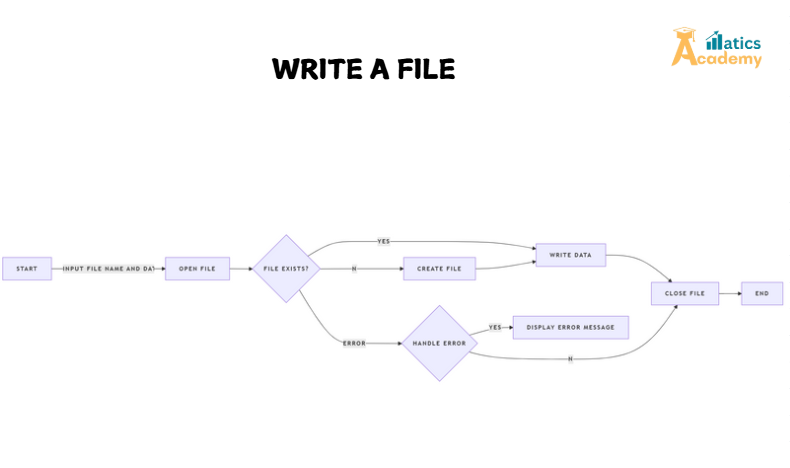
To write to a file in Python, the open() function is used. You specify the mode you want to open the file in—usually "w" for writing or "a" for appending. Here’s the general syntax:
file = open("filename.txt", "w") # Open the file in write mode
file.write("Hello, world!") # Write data to the file
file.close() # Close the file
File Modes for Writing
There are several modes you can use when opening a file for writing:
"w": Write mode. If the file exists, it will overwrite the content. If the file does not exist, a new file will be created."a": Append mode. If the file exists, it will append the new data at the end without modifying the existing content."x": Exclusive creation mode. It creates a new file, but if the file already exists, it will raise aFileExistsError.
Example 1: Writing Text to a File
Let’s write some text to a file using "w" mode:
# Open the file in write mode
file = open("greetings.txt", "w")
# Write some content
file.write("Hello, this is a simple file writing example!\n")
file.write("We can add more lines as well.\n")
# Close the file
file.close()
print("Content written to file successfully.")
Explanation:
- The file
greetings.txtwill be created (if it doesn’t exist). - The text will be written to the file, and the file will be closed afterward.
Example 2: Appending to a File
If you want to add content to an existing file without deleting its previous content, you can use the "a" mode (append mode):
# Open the file in append mode
file = open("greetings.txt", "a")
# Append some content
file.write("This line is added after the previous content.\n")
# Close the file
file.close()
print("Content appended to file successfully.")
Explanation:
- The content
"This line is added after the previous content."will be appended to the filegreetings.txt, without removing the existing content.
Example 3: Writing Multiple Lines Using writelines()
You can write multiple lines to a file at once using the writelines() method, which accepts a list of strings:
# Open the file in write mode
file = open("greetings.txt", "w")
# List of lines to write to the file
lines = ["Line 1: Hello, World!\n", "Line 2: Python file handling is easy.\n", "Line 3: Writing is fun!\n"]
# Write the list of lines to the file
file.writelines(lines)
# Close the file
file.close()
print("Multiple lines written to file successfully.")
Explanation:
- The
writelines()method writes each string in the list to the file as a new line. The\nat the end of each string ensures that the lines are written correctly with line breaks.
Best Practices for Writing to Files
- Always Close the File: After writing to a file, always close it to ensure the changes are saved properly. You can use
file.close()to close the file. - Using
withStatement: Thewithstatement automatically handles file closing, even if an error occurs within the block.pythonCopy codewith open("greetings.txt", "w") as file: file.write("This file is automatically closed after the block.")Using thewithstatement is a cleaner and more efficient way to handle file operations. - Check File Permissions: Ensure that the file you’re trying to write to has the correct permissions for writing. If the file is read-only or you don’t have permission to write, Python will raise a
PermissionError. - Error Handling: It’s good practice to handle potential errors using
tryandexceptblocks, such as dealing with cases where the file is not found or when there’s an issue with the disk.pythonCopy codetry: with open("greetings.txt", "w") as file: file.write("Error handling example!") except PermissionError: print("You do not have permission to write to this file.")
Mini Project: Log File for User Activities
Let’s create a simple log file to track user activities. In this mini-project, we’ll:
- Write user activities (like login, view page, etc.) to a file.
- Append new activities without overwriting old ones.
# Mini Project: User Activity Log
def log_activity(activity):
with open("user_activity_log.txt", "a") as file:
file.write(f"{activity}\n")
# Simulate some user activities
log_activity("User logged in.")
log_activity("User viewed the homepage.")
log_activity("User added an item to the cart.")
log_activity("User logged out.")
print("User activities have been logged.")
Explanation:
- The
log_activity()function appends each new activity to the fileuser_activity_log.txt. - We simulate different user actions like logging in, viewing pages, and logging out.
- Each activity is written to the file in a new line.
Interview Questions and Answers on File Handling
Amazon
Q1: How can you handle file writing operations in a way that ensures data is not lost during unexpected program termination?
A1: You can write to files in an incremental manner, for example by appending data rather than overwriting it. Additionally, you can use the with statement to automatically close the file after writing, which ensures that all data is saved, even in the event of a program crash.
Q2: What is the advantage of using the with statement when writing to files?
A2: The with statement automatically closes the file once the block of code is completed, even if an exception occurs. This ensures proper resource management and avoids memory leaks or file corruption.
Zoho
Q3: Can you write binary data to a file in Python?
A3: Yes, you can open a file in binary write mode (wb) to write binary data. This is useful when working with image files, audio files, or any data that is not plain text.
Infosys
Q4: What is the difference between the write() and writelines() methods in Python file handling?
A4: The write() method writes a single string to the file, whereas writelines() writes a list of strings to the file. Each string in the list is written consecutively.
TCS
Q5: How would you handle a situation where the program does not have permission to write to a file?
A5: You can use a try-except block to catch a PermissionError and handle it appropriately, such as informing the user that they do not have write permissions or requesting elevated privileges.
Conclusion
Writing to files is a crucial skill in Python programming, allowing you to store and manipulate data persistently. By using Python’s built-in file handling methods and following best practices, you can effectively manage files for your applications. From simple text files to complex logs, file handling is a fundamental concept that every Python developer must understand.
Write to File
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
