Introduction
Pointer Arithmetic in C is a powerful feature in C programming that allows manipulation of memory addresses stored in pointers. Understanding pointer arithmetic is essential for efficient memory management, dynamic data structures, and system-level programming.
Why Learn Pointer Arithmetic in C?
- Efficient Memory Traversal: Quickly access elements in arrays.
- Dynamic Memory Management: Move between memory locations dynamically.
- Foundation for Data Structures: Enables efficient implementation of linked lists, trees, etc.
- System-Level Programming: Essential for low-level programming like writing device drivers.
Pointer Arithmetic in C Operations
Pointer arithmetic works based on the size of the data type that the pointer points to. Common operations include:
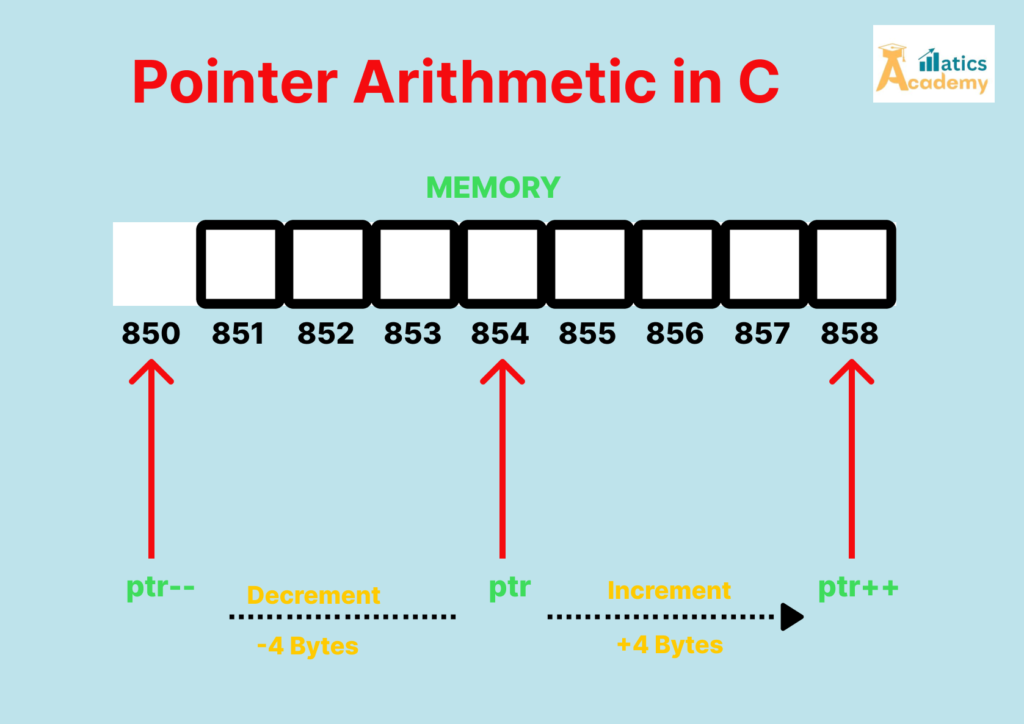
- Incrementing a Pointer (
ptr++)- Moves the pointer to the next memory location based on the data type size.
- Example: If a pointer points to an
int(4 bytes), incrementing it adds 4 to its address.
- Decrementing a Pointer (
ptr--)- Moves the pointer to the previous memory location.
- Adding an Integer to a Pointer (
ptr + n)- Moves the pointer forward by
nelements.
- Moves the pointer forward by
- Subtracting an Integer from a Pointer (
ptr - n)- Moves the pointer backward by
nelements.
- Moves the pointer backward by
- Subtracting Two Pointers (
ptr1 - ptr2)- Calculates the number of elements between two pointers.
Syntax
Pointer arithmetic uses standard operators such as +, -, ++, --, etc.
Example
data_type *pointer; pointer++; pointer += n; pointer--; pointer -= n;
Example: Pointer Arithmetic with Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int *ptr = arr; // Pointer to the first element of the array
printf("Initial pointer address: %p, Value: %d\n", ptr, *ptr);
ptr++; // Increment pointer
printf("After incrementing: %p, Value: %d\n", ptr, *ptr);
ptr += 2; // Move pointer 2 steps forward
printf("After adding 2: %p, Value: %d\n", ptr, *ptr);
ptr--; // Decrement pointer
printf("After decrementing: %p, Value: %d\n", ptr, *ptr);
return 0;
}
Output:
Initial pointer address: 0x7ffe123abcd, Value: 10
After incrementing: 0x7ffe123abce, Value: 20
After adding 2: 0x7ffe123abd0, Value: 40
After decrementing: 0x7ffe123abcf, Value: 30 Pointer Arithmetic in C Rules
- Scaling by Data Type Size: Pointer arithmetic scales the address changes by the size of the data type. For example:
- If a pointer points to an
int(4 bytes),ptr + 1increments the address by 4 bytes. - If a pointer points to a
char(1 byte),ptr + 1increments the address by 1 byte.
- If a pointer points to an
- Valid Memory Access: Ensure that pointer arithmetic does not access memory outside the allocated range to avoid segmentation faults.
- Arithmetic Only with Same Type: Operations like
ptr1 - ptr2are valid only for pointers pointing to the same type.
Example: Traversing an Array Using Pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 10, 15, 20, 25};
int *ptr = arr; // Pointer to the first element of the array
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Array elements using pointer arithmetic:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("Element %d: %d (Address: %p)\n", i, *(ptr + i), ptr + i);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Array elements using pointer arithmetic:
Element 0: 5 (Address: 0x7ffe123abcd)
Element 1: 10 (Address: 0x7ffe123abce)
Element 2: 15 (Address: 0x7ffe123abcf)
Element 3: 20 (Address: 0x7ffe123abd0)
Element 4: 25 (Address: 0x7ffe123abd1) Pointer Subtraction Example
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int *ptr1 = &arr[2]; // Pointer to the 3rd element
int *ptr2 = &arr[0]; // Pointer to the 1st element
printf("Number of elements between ptr1 and ptr2: %ld\n", ptr1 - ptr2);
return 0;
}
Output:
Number of elements between ptr1 and ptr2: 2Common Mistakes in Pointer Arithmetic in C
- Out-of-Bounds Access: Performing arithmetic that moves the pointer outside the allocated memory range.
- Pointer Type Mismatch: Ensure the pointer’s type matches the operations being performed.
- Uninitialized Pointers: Leads to undefined behavior when used in arithmetic.
Conclusion
Pointer Arithmetic in Cis a fundamental concept for working efficiently with arrays, dynamic memory, and advanced data structures. Mastering these operations opens up the full potential of C programming for memory manipulation and system-level programming.
Interview Questions
1. What is a pointer?
Company: Infosys
Answer:
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable.
2. What is the syntax for declaring a pointer?
Company: TCS
Answer:
The syntax is: data_type *pointer_name;
For example: int *ptr; declares a pointer to an integer.
3. What happens if you dereference an uninitialized Pointer Arithmetic in C?
Company: Cognizant
Answer:
Dereferencing an uninitialized pointer leads to undefined behavior, which may cause a program crash.
4. How do you assign an address to a Pointer Arithmetic in C?
Company: Wipro
Answer:
Use the & (address-of) operator:
int x = 10; int *ptr = &x;
5. What is a null pointer, and why is it used in Pointer Arithmetic in C?
Company: HCL Technologies
Answer:
A null pointer is a pointer that does not point to any valid memory location. It is useful for checking if a pointer has been assigned a valid address.
Quizzes
Pointer Arithmetic in C Quiz
