The break statement in pythonallows you to stop a loop (whether it’s a for or while loop) before it finishes its natural cycle. This is useful when a specific condition is met, and you no longer need to continue the loop.
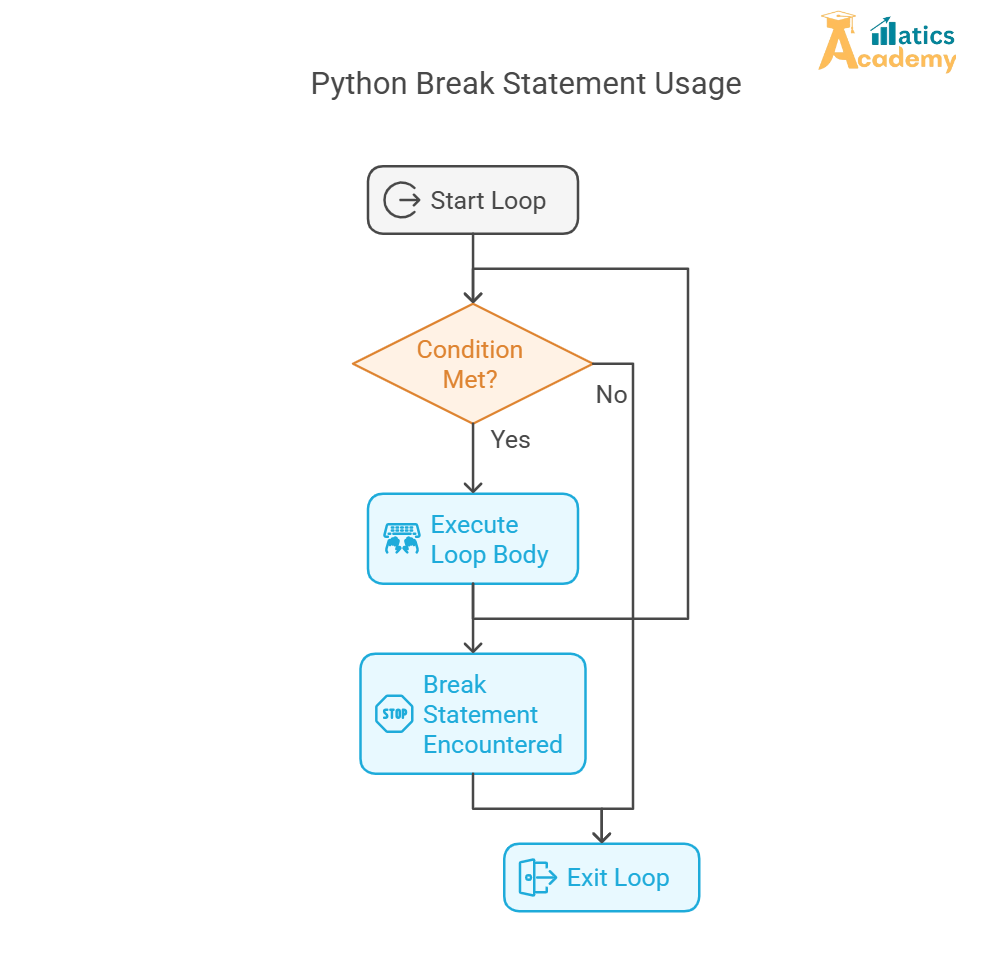
Table of Contents
- What is the break statement in python?
- Syntax of the break statement in python
- Example of Using the break statement in python
- Using
breakin aforLoop - Using
breakin awhileLoop - Using
breakin Nested Loops - Common Mistakes with
break - Mini-Project: Finding the First Prime Number
- Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is the break statement in python?
The break statement immediately stops the nearest loop when a condition is met, and the program moves to the next line of code after the loop.
2. Syntax of the break statement in python
The break statement is simple. You just need to write:
break
It’s often used inside a conditional statement in a loop to exit early.
3. Example of Using the break statement in python
Here’s a simple example that stops the loop when i equals 3:
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
The loop stops when i becomes 3.
4. Using break in a for Loop
You can also use break in a for loop to stop early when a condition is met:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for fruit in fruits:
if fruit == "banana":
break
print(fruit)
Output:
apple
The loop stops when it encounters “banana”.
5. Using break in a while Loop
break works in a while loop too. Here’s an example:
i = 0
while i < 5:
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
i += 1
Output:
0
1
2
The loop stops when i equals 3.
6. Using break in Nested Loops
If you use break in nested loops, it only exits the inner loop:
or i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
if j == 2:
break
print(f"i={i}, j={j}")
Output:
i=0, j=0
i=0, j=1
i=1, j=0
i=1, j=1
i=2, j=0
i=2, j=1
The inner loop breaks when j is 2, but the outer loop keeps going.
7. Common Mistakes with break
- Unintended Exit: Make sure your
breakcondition is correct to avoid exiting the loop too early. - Nested Loops:
breakonly stops the innermost loop. If you need to break out of multiple loops, use flags or another control method.
8. Mini-Project: Finding the First Prime Number
Let’s write a program that finds the first prime number greater than 1:
def find_prime():
num = 2
while True:
for i in range(2, num):
if num % i == 0:
break
else:
print(f"The first prime number is {num}")
break
num += 1
find_prime()
Output:
The first prime number is 2
Interview Questions and Answers
- Q: How does the
breakstatement work in Python? - A: The
breakstatement stops the nearest loop and moves the program to the next line of code after the loop.
Amazon
- Q: Can a break statement in python be used in both
forandwhileloops? - A: Yes, it can be used in both types of loops to exit when a condition is met.
TCS
- Q: What happens if a break statement in python is used in a
whileloop? - A: It immediately exits the loop and continues with the next line of code after the loop.
Infosys
- Q: Can
breakbe used in nested loops? - A: Yes, but it only exits the innermost loop. To break out of multiple loops, use flags or other techniques.
Zoho
- Q: How can you stop an infinite loop using
break? - A: You can stop an infinite loop with
breakby adding a condition to exit the loop.
Conclusion
The break statement is a useful tool to control loop execution. It helps you exit loops early when certain conditions are met, making your code more efficient and clean.ython, used to control the flow of execution in programs. By understanding how to use these effectively, you can handle repetitive tasks and break out of loops efficiently, enabling you to write cleaner, more efficient code.
break-statement
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
