Introduction to Date Time API in Java
Working with dates and times in Java has always been essential, especially for applications involving scheduling, timestamps, and data validation. Moreover, Java’s Date Time API, introduced in Java 8, provides a much more robust and intuitive framework for handling date and time. This is especially important for developers who need to write code that’s clear, reliable, and maintains compatibility across time zones.

Why Study the Date Time API In Java?
In real-world applications, dealing with date and time often involves complex calculations, such as finding intervals between two dates or adjusting for different time zones. Therefore, the Date Time API simplifies these tasks with a structured and user-friendly approach. In addition, understanding this API is beneficial for career growth in software development, as date and time management is a core skill in many applications.
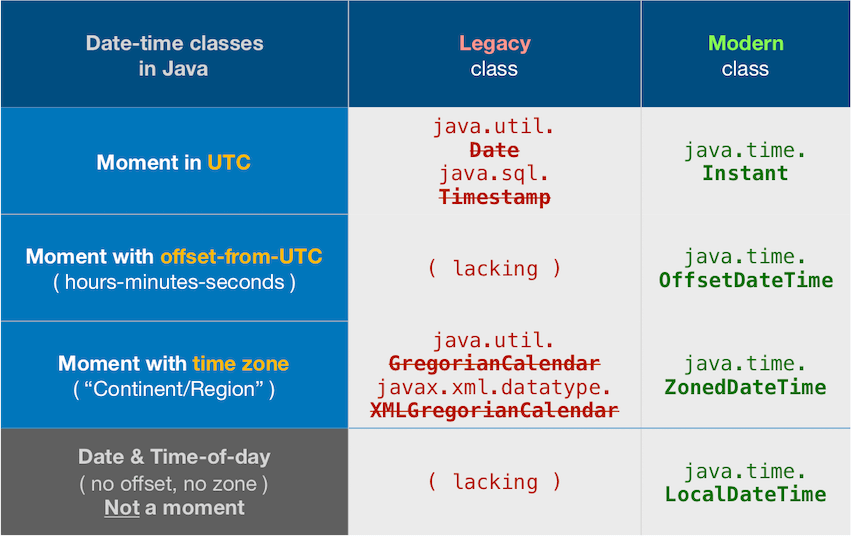
What Will Be Covered?
This guide will cover:
- Basic Date and Time Classes: An overview of the essential classes like
LocalDate,LocalTime, andLocalDateTime. - Formatting and Parsing: Techniques to format dates and times and parse strings.
- Time Zones and Offsets: Handling time zones with
ZonedDateTimeandOffsetDateTime. - Advanced Manipulation: Working with durations, periods, and calculations.
Detailed Content
Basic Date and Time Classes
The Date Time API introduces several classes that make it easy to work with dates and times separately. For example, LocalDate handles date-only values without time, while LocalTime focuses on time without dates. Furthermore, LocalDateTime combines both, providing a complete date and time structure without time zone information.
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Date: " + date);
System.out.println("Time: " + time);
System.out.println("DateTime: " + dateTime);Formatting and Parsing Dates and Times
Often, you need to display dates and times in a specific format, or parse user input into date objects. To address this, the Date Time API includes the DateTimeFormatter class, allowing flexible formatting and parsing. Not only does this make the code readable, but it also prevents errors related to inconsistent date formats.
Example :
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm");
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String formattedDateTime = dateTime.format(formatter);
System.out.println("Formatted DateTime: " + formattedDateTime);Working with Time Zones and Offsets
When working with global applications, handling time zones is crucial. Thus, the Date Time API provides classes like ZonedDateTime and OffsetDateTime to manage different time zones and offsets effectively. Additionally, these classes ensure consistency in time representations across different regions.
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
System.out.println("ZonedDateTime: " + zonedDateTime);Manipulating Dates and Times
In many cases, you might need to perform calculations, such as finding the duration between two times or adding days to a date. To make this simpler, the Date Time API offers methods for date and time manipulation. For instance, Period represents a period between dates, while Duration handles time intervals.
Example :
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate date2 = date1.plusDays(5);
Period period = Period.between(date1, date2);
System.out.println("Days difference: " + period.getDays());Summary
In summary, the Date Time API in Java introduces a powerful way to handle dates and times, from basic date management to complex time zone handling. As a result, developers can write code that is both reliable and efficient for any date or time-related functionality.
Learning Outcomes
After completing this topic, learners will be able to:
- Understand and use the core date and time classes.
- Format and parse date-time objects.
- Work with different time zones.
- Perform date and time calculations.
Common Interview Questions
What is the difference between LocalDateTime and ZonedDateTime?
Answer: LocalDateTime represents a date and time without a time zone, while ZonedDateTime includes time zone information.
How can you parse a date from a string in a specific format?
Answer: By using DateTimeFormatter with a pattern, you can parse strings into LocalDate, LocalTime, or LocalDateTime objects.
What is the purpose of the Period and Duration classes?
Answer: Period represents date-based amounts like years, months, or days, while Duration represents time-based amounts like hours, minutes, or seconds.
Practice Exercises
- Convert a given date to a different time zone.
- Calculate the number of days between two dates.
- Format a date-time in the pattern “yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm”.
Additional Resources
- Java Documentation on Date Time API – Official Oracle Java documentation.
- Effective Java by Joshua Bloch – Contains best practices for using the Date Time API.
Date Time API
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
