File handling in Python allows developers to interact with files stored on the system. It is an essential feature for managing data persistently, enabling operations such as reading, writing, and modifying file content. Whether working with configuration files, log files, or structured data formats like CSV or JSON, mastering file handling is critical for efficient programming.
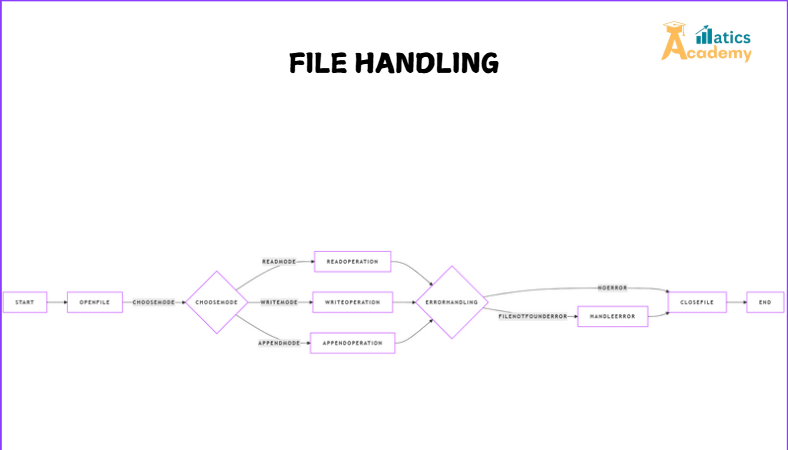
This guide will cover the fundamentals of file handling in Python, practical applications, error handling, and more.
What Is File Handling in Python?
File handling refers to the process of performing operations like opening, reading, writing, appending, and closing files. Python provides built-in functions to simplify these operations, making it user-friendly and efficient.
Types of File Operations
- Opening a File: Using the
open()function. - Reading a File: Fetching file content.
- Writing to a File: Overwriting or creating new content.
- Appending to a File: Adding content without deleting existing data.
- Closing a File: Ensuring all changes are saved and resources are freed.
Opening a File
In Python, the open() function is used to open files. Its syntax is:
file_object = open("filename", "mode")
File Modes
"r": Read (default mode) – Opens the file for reading. Raises an error if the file doesn’t exist."w": Write – Opens the file for writing, truncating it if it exists or creating a new one."a": Append – Opens the file for appending new content."rb": Read in binary mode."wb": Write in binary mode.
Reading from a File
You can read a file’s content using the following methods:
read(): Reads the entire file content as a string.readline(): Reads a single line.readlines(): Reads all lines and returns them as a list.
Example: Reading File Content
file = open("example.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()
Writing to a File
To write data into a file, use the write() method. The file must be opened in "w" or "a" mode.
Example: Writing to a File
file = open("example.txt", "w")
file.write("This is a new file.")
file.close()
Appending to a File
Appending content to a file does not overwrite existing data. Use "a" mode to append text.
Example: Appending to a File
file = open("example.txt", "a")
file.write("\nThis line is added at the end.")
file.close()
File Handling in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
After completing file operations, always close the file using the close() method to ensure all changes are saved.
Example
file = open("example.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
file.close()
Alternatively, you can use the with statement, which automatically closes the file:
with open("example.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read()
Error Handled in File handling Operations
Python provides robust mechanisms for handle the file-related errors. Common exceptions include:
FileNotFoundError: Raised when a file does not exist.PermissionError: Raised when the program lacks permission to access a file.
Example: Using Try-Except for Error Handling
try:
file = open("nonexistent_file.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
print("The file does not exist.")
finally:
file.close()
Practical Applications of File Handling
1. Logging System
Keep track of application events by appending logs to a file.
2. Data Storage
Store configuration data or results persistently using file handling.
3. CSV File Processing
Use Python’s csv module to handle structured data efficiently.
Mini-Project: To-Do List Application
In this mini-project, we’ll build a console-based To-Do List Application using file handling. The application will:
- Load tasks from a file.
- Allow users to add, delete, or view tasks.
- Save tasks persistently in a file.
Code Implementation
NOTE: It’s better to run in the interpreter (vscode or Pycharm)
# Function to load tasks from the file
def load_tasks():
try:
with open("tasks.txt", "r") as file:
tasks = file.readlines()
return [task.strip() for task in tasks]
except FileNotFoundError:
# If the file doesn't exist, return an empty list
return []
# Function to save tasks to the file
def save_tasks(tasks):
with open("tasks.txt", "w") as file:
for task in tasks:
file.write(task + "\n")
# Function to add a new task
def add_task(tasks, task):
tasks.append(task)
save_tasks(tasks)
print(f"Task '{task}' added.")
# Function to delete a task
def delete_task(tasks, task):
if task in tasks:
tasks.remove(task)
save_tasks(tasks)
print(f"Task '{task}' deleted.")
else:
print(f"Task '{task}' not found.")
# Function to view all tasks
def view_tasks(tasks):
if not tasks:
print("No tasks available.")
else:
print("\nTo-Do List:")
for i, task in enumerate(tasks, 1):
print(f"{i}. {task}")
# Main program loop
def main():
print("Welcome to the To-Do List Application!")
tasks = load_tasks()
while True:
print("\nMenu:")
print("1. Add Task")
print("2. View Tasks")
print("3. Delete Task")
print("4. Exit")
choice = input("Choose an option: ")
if choice == "1":
task = input("Enter the task: ")
add_task(tasks, task)
elif choice == "2":
view_tasks(tasks)
elif choice == "3":
task = input("Enter the task to delete: ")
delete_task(tasks, task)
elif choice == "4":
print("Exiting the application. Goodbye!")
break
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
How It Works
- Loading Tasks:
Theload_tasks()function reads tasks fromtasks.txt. If the file does not exist, it handles theFileNotFoundErrorby returning an empty list. - Saving Tasks:
Thesave_tasks()function writes the current list of tasks totasks.txt, ensuring persistence. - Adding a Task:
Theadd_task()function appends a new task to the list and callssave_tasks()to update the file. - Deleting a Task:
Thedelete_task()function removes a task from the list if it exists and updates the file. - Viewing Tasks:
Theview_tasks()function displays all tasks with an index. - Menu Navigation:
Themain()function provides a menu-driven interface for the user.
Interview Questions and Answers
Amazon
Q1: What are the advantages of using the with statement in file handling?
A1: The with statement ensures that the file is automatically closed after the block of code is executed, even if an error occurs.
Q2: How can you read large files efficiently in Python?
A2: Use a for loop to iterate over the file object line by line, as this does not load the entire file into memory.
TCS
Q3: How do you handle encoding issues in file handling?
A3: Specify the encoding explicitly using the encoding parameter, e.g., open("file.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8").
Infosys
Q4: How do you write a list of strings to a file?
A4: Use the writelines() method:
lines = ["Line 1\n", "Line 2\n", "Line 3\n"]
with open("file.txt", "w") as file:
file.writelines(lines)
Conclusion
File handling in Python is an indispensable skill for developers. By mastering file operations and understanding how to handle errors effectively, you can build robust applications that interact seamlessly with the file system.
File Handling
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
