The for loop is one of the most commonly used loops in Python for iterating over sequences such as lists, tuples, dictionaries, strings, or ranges. Unlike while loops, which are condition-based, for loops are used to iterate a specific number of times or over a sequence of items.
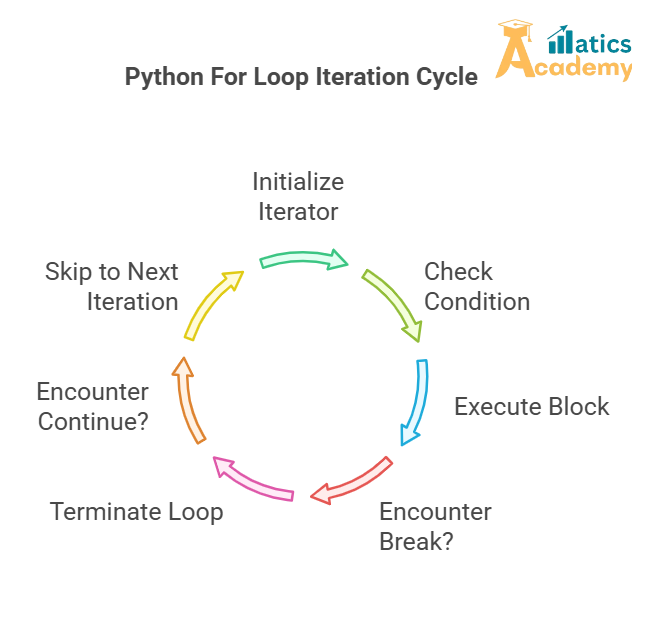
Table of Contents
- What is a For Loop?
- Syntax of a For Loop
- Example of a Simple For Loop
- Looping Through a List
- Looping Through a String
- Using the
range()Function - Nested For Loops
- Break and Continue Statements in For Loops
- Common Pitfalls with For Loops
- Mini-Project: Sum of Even Numbers
- Interview Questions and Answers (Google, Amazon, TCS, Infosys, Zoho)
1. What is a For Loop?
A for loop is a control flow statement used to repeatedly execute a block of code a specified number of times or for each item in a sequence (such as a list or string). It helps you iterate over sequences, making it simpler to perform repetitive tasks like processing items or numbers in a series.
2. Syntax of a For Loop
The syntax of a for loop in Python is:
for variable in sequence:
# Code to execute
variable: A temporary variable that takes the value of each item in the sequence during each iteration.sequence: A collection of items (like a list, string, or range) to loop through.- Code block: The code inside the loop that will execute on each iteration.
3. Example of a Simple For Loop
Let’s start with a basic example of iterating through a list of numbers.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for num in numbers:
print(num)
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
Here, the for loop iterates over the list numbers and prints each number one by one.
4. Looping Through a List
One of the most common uses of for loops is to iterate through lists.
Example:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
Output:
apple
banana
cherry
This loop goes through each item in the fruits list and prints it.
5. Looping Through a String
You can also use a for loop to iterate over the characters of a string.
Example:
word = "Python"
for letter in word:
print(letter)
Output:
P
y
t
h
o
n
Here, the loop iterates over each character in the string word and prints it.
6. Using the range() Function
The range() function is commonly used in a for loop to generate a sequence of numbers. It can be used with one, two, or three arguments:
range(stop): Generates numbers from0tostop-1.range(start, stop): Generates numbers fromstarttostop-1.range(start, stop, step): Generates numbers fromstarttostop-1, with a given step.
Example 1: Using range(stop)
for i in range(5):
print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
Example 2: Using range(start, stop)
for i in range(2, 6):
print(i)
Output:
2
3
4
5
Example 3: Using range(start, stop, step)
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i)
Output:
0
2
4
6
8
7. Nested For Loops
You can also use a for loop inside another for loop. This is called a nested for loop.
Example:
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
print(f"i = {i}, j = {j}")
Output:
i = 0, j = 0
i = 0, j = 1
i = 0, j = 2
i = 1, j = 0
i = 1, j = 1
i = 1, j = 2
i = 2, j = 0
i = 2, j = 1
i = 2, j = 2
In this example, the outer loop runs 3 times, and for each iteration of the outer loop, the inner loop runs 3 times.
8. Break and Continue Statements in For Loops
You can control the flow of a for loop using the break and continue statements:
break: Exits the loop completely.continue: Skips the current iteration and moves to the next one.
Example with break:
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
In this example, the loop exits when i equals 3 due to the break statement.
Example with continue:
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
4
Here, the loop skips printing 3 due to the continue statement and proceeds with the next iteration.
9. Common Pitfalls with For Loops
- Infinite Loops: Be cautious when using loops, especially when the loop conditions are not properly set, as they can cause infinite loops.
- Off-by-One Error: Pay attention to how the
range()function works, as you may inadvertently miss or include an item by setting incorrect start, stop, or step values.
10. Mini-Project: Sum of Even Numbers
Let’s create a simple program that calculates the sum of all even numbers from 1 to 100 using a for loop.
Objective:
The program will:
- Loop through numbers from 1 to 100.
- Check if each number is even (divisible by 2).
- Sum the even numbers and print the result.
def sum_even_numbers():
total = 0
for i in range(1, 101):
if i % 2 == 0:
total += i
print(f"The sum of even numbers from 1 to 100 is {total}")
sum_even_numbers()
Sample Output:
The sum of even numbers from 1 to 100 is 2550
Interview Questions and Answers
Q: How does a for loop work in Python?
A: A for loop iterates over a sequence (like a list, string, or range). In each iteration, it assigns the current item to a loop variable and executes the code block inside the loop.
Amazon
Q: Can you use a for loop with a dictionary?
A: Yes, you can iterate through a dictionary using the for loop. For example, you can loop through the keys, values, or both:
my_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
for key, value in my_dict.items():
print(key, value)
TCS
Q: What is the difference between for and while loops in Python?
A: A for loop is used when you know the number of iterations or when iterating over a sequence, while a while loop is used when you want to repeat an action until a certain condition is met.
Infosys
Q: What happens if you forget to increment a variable inside a for loop?
A: If you forget to increment the loop variable, the loop might run indefinitely if there is no terminating condition or it might produce incorrect results.
Zoho
Q: Can a for loop be used to iterate over multiple variables?
A: Yes, you can iterate over multiple variables using the zip() function or multiple for loops:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = ['a', 'b', 'c']
for x, y in zip(a, b):
print(x, y)
Conclusion
The for loop is a powerful tool in Python for iterating over sequences and repeating tasks efficiently. By understanding how to use for loops with different data structures (like lists, strings, and ranges), you can automate repetitive tasks and handle complex iteration scenarios with ease. Combining loops with break, continue, and range() can further enhance your ability to manage loops effectively.
for loops
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
