Introduction
In C programming, functions are an essential building block that help you write organized, modular, and reusable code. A function is a self-contained block of code designed to perform a specific task. Instead of repeating code multiple times, you can call a function whenever needed, improving program efficiency and readability.
In this guide, we will cover the basics of functions in C, their types, syntax, examples, advantages, and best practices to master them.
What is a Function in C?
A function in C is a group of statements that perform a specific task. When the function is called, the program control jumps to the function, executes the statements inside it, and then returns to the point where it was called.
Functions help break large programs into smaller, manageable pieces, making them easier to debug, maintain, and understand.
Syntax of a Function in C
return_type function_name(parameters) {
// body of the function
}Key parts of a function:
return_type: The data type of the value the function returns (e.g., int, float, void).function_name: The name of the function.parameters: Inputs to the function (also known as arguments).
Example of a Function in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function declaration
int add(int a, int b);
int main() {
int result;
result = add(5, 7); // Function call
printf("Sum = %d", result);
return 0;
}
// Function definition
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}Output:
Sum = 12
Types of Functions in C
Functions in C are mainly categorized into two types:
- Library Functions
- Predefined functions provided by C libraries.
- Example:
printf(),scanf(),sqrt(), etc.
- User-Defined Functions
- Functions created by the programmer to perform specific tasks.
- Example:
int add(int a, int b),void display(), etc.
Benefits of Using Functions in C
- Reusability: Write once, use multiple times without rewriting the code.
- Modularity: Divide the program into smaller, logical units.
- Easy Maintenance: Easier to modify and update specific parts.
- Better Debugging: Helps in isolating and fixing bugs faster.
- Code Readability: Improves the overall structure and readability of your code.
How Function Calls Work in C
How Function Calls Work in C
1. Function Invocation:
When a function is called, the program immediately transfers control to that function. This marks the start of the function execution.
2. Argument Passing:
Next, the values or variables passed during the function call are assigned to the function’s parameters, enabling the function to process them.
3. Function Execution:
Then, the code inside the function body runs, performing the specific task defined using the passed parameters.
4. Control Transfer Back:
After executing the function logic, the control flows back to the calling point in the main program.
5. Return Value Handling:
If the function returns a value, the program receives and handles that value at the call site.
Important Concepts Related to Functions
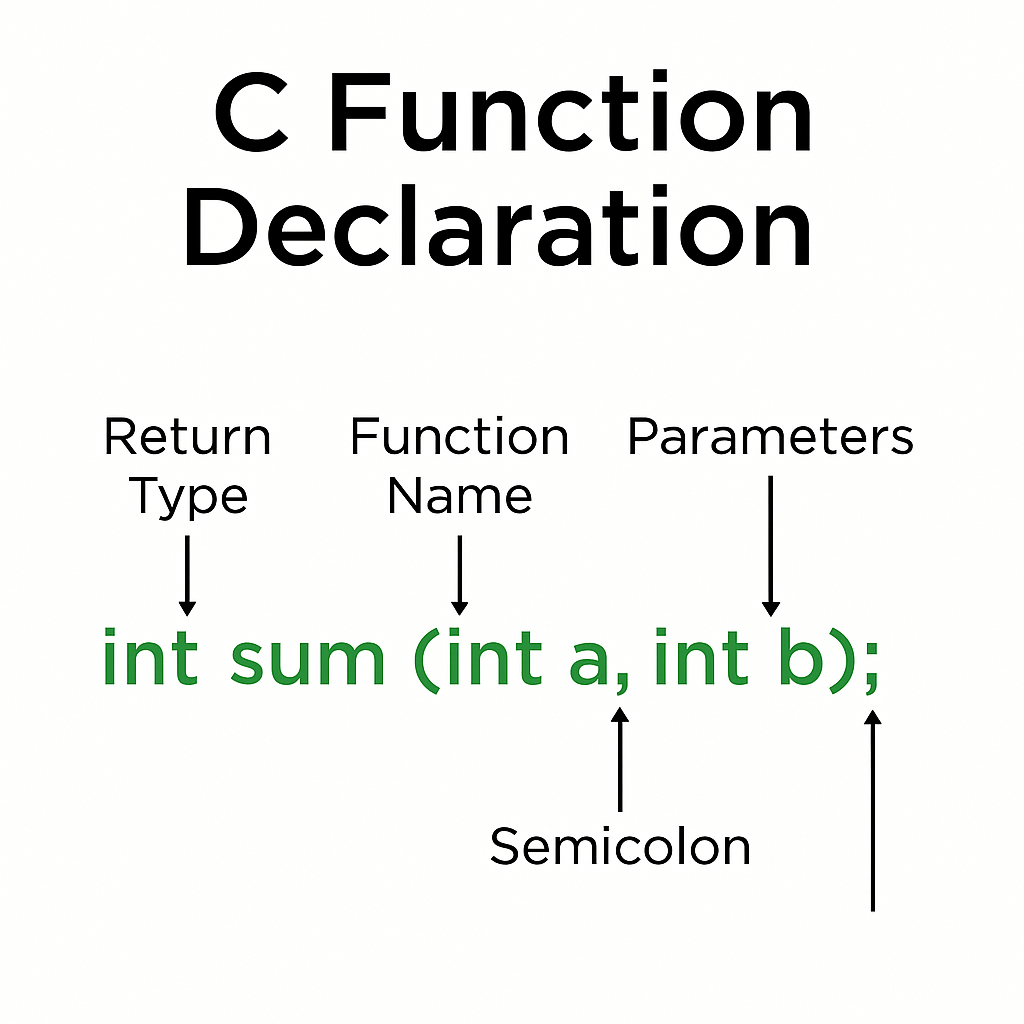
Function Declaration (Prototype)
Before using a function, it must be declared. This informs the compiler about the function’s name, return type, and parameters.
Example:
int add(int, int);
Function Definition
The function’s body contains the actual logic
Function Call
The program calls the function at this point.
Best Practices for Functions in C
- Always use meaningful function names.
- Keep functions small and focused on a single task.
- Document the purpose of each function with comments.
- To ensure proper declaration before use, always use function prototypes.
- Moreover, avoid using global variables inside functions unless absolutely necessary, as they can make your code harder to maintain and debug.
Conclusion
Functions in C programming play a crucial role in creating organized, efficient, and easy-to-maintain code. They allow you to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable tasks, improving both the structure and clarity of your programs.
Importance of Functions in C Programming
By mastering how to declare, define, and use functions, you can elevate your programming skills. Functions contribute significantly to:
- Code Reusability: Once defined, functions can be used multiple times, saving time and reducing redundancy.
- Modularity: Functions allow you to split your program into smaller, independent modules, which enhances code readability and maintainability.
- Debugging: When issues arise, it’s easier to debug smaller chunks of code (functions) rather than a large, monolithic program.
Tips for Mastering Functions
To become proficient with functions:
- Practice Function Declaration: Always use function prototypes to declare functions before using them in the program.
- Understand Scope: Be aware of local and global variable scope when designing functions.
- Pass Arguments Carefully: Understand the difference between pass-by-value and pass-by-reference for efficient argument passing.
Interview Questions
1. What are the different types of functions in C programming?(HCL)
In C programming, functions fall into two main categories: library functions and user-defined functions. Firstly, library functions are built-in functions provided by the C standard library. Common examples include printf(), scanf(), and sqrt(). Since library functions are precompiled and thoroughly tested, they help developers save considerable time and effort. In contrast, programmers create user-defined functions to perform specific tasks that meet the needs of their applications.By organizing code into such custom functions, developers can improve modularity, reusability, and overall clarity.
2.Why are function prototypes important in C? (IBM)
Function prototypes play a critical role in C programming. To ensure the compiler recognizes a function before its usage, programmers use a function prototype, which declares the function before it is defined or called in the program.. It informs the compiler about the function’s name, return type, and the types of its parameters
3.What is the difference between call by value and call by reference in C? (AMAZON)
In C, a function receives arguments through two main methods: call by value and call by reference. In the call by value method, the function receives a copy of the actual variable’s value, so any changes made inside the function do not affect the original variable. Changes made to the parameter inside the function do not affect the original value outside the function.
4.Can a function return multiple values in C? (Meta)
In standard C programming, a function can only return a single value directly using the return statement. However, programmers can achieve the effect of returning multiple values by other means. One common approach is using pointers—passing multiple pointer arguments to the function, allowing it to modify the original variables’ values
5.What error does a C compiler produce when you call a function without declaring or defining it first? (FB)
If you call a function in C before declaring or defining it, the compiler cannot recognize the function signature, which leads to a compilation error As a result, a compilation error will occur, typically showing an error message like “undefined reference to function.” This issue arises because, in C, the compiler requires knowledge of the function’s signature, including its return type, name, and parameters, before it can properly link the function during the compilation process.
learn more about c
Lets play..!
