The if statement is one of the fundamental building blocks in decision making. It allows a program to test conditions and execute certain code if the condition evaluates to True. The if statement is crucial in controlling the flow of the program and is used in conjunction with elif and else to make more complex decisions.
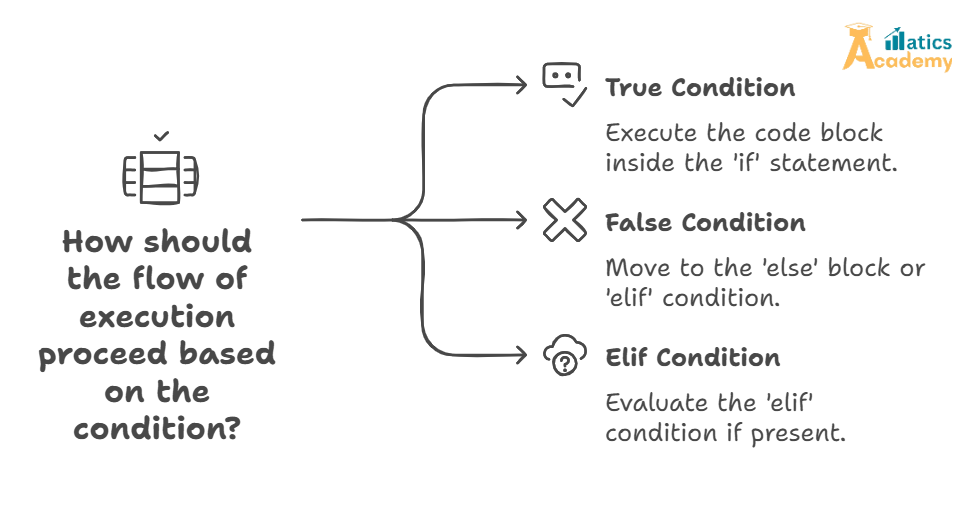
Table of Contents
- What is an
ifStatement? - Syntax of the
ifStatement - Example of a Simple
ifStatement - Nested
ifStatements - Using Multiple Conditions in
ifStatements- Logical Operators (
and,or,not)
- Logical Operators (
- The
if-elseandif-elif-elseStatements - Common Pitfalls with
ifStatements - Mini-Project: Even or Odd Number Checker
- Interview Questions and Answers (Google, Amazon, TCS, Infosys, Zoho)
1. What is an if Statement?
The if statement is used to test a condition and execute a block of code only if the condition is True. If the condition is False, the code inside the if block will be skipped. The if statement is a basic control flow tool that enables decision-making capabilities in Python programs.
2. Syntax of the if Statement
The basic syntax of an if statement looks like this:
if condition:
# Code to execute if condition is True
condition: An expression that evaluates toTrueorFalse.- The code block inside the
ifstatement will execute only if the condition evaluates toTrue.
Example:
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult.")
Here, the program checks if the age is greater than or equal to 18, and if so, it prints "You are an adult.".
3. Example of a Simple if Statement
Let’s take a simple example to demonstrate how the if statement works.
number = 10
if number > 5:
print("The number is greater than 5.")
Output:
The number is greater than 5.
In this case, the condition number > 5 is True, so the print statement is executed.
4. Nested if Statements
A nested if statement is an if statement inside another if statement. This allows for more complex decision-making.
Example:
age = 20
is_student = True
if age >= 18:
if is_student:
print("You are an adult student.")
else:
print("You are an adult, but not a student.")
else:
print("You are a minor.")
Here:
- The outer
ifchecks if the person is 18 or older. - The inner
ifchecks if the person has a voter ID.
This helps in making decisions based on multiple conditions.
5. Using Multiple Conditions in if Statements
Python allows combining multiple conditions within an if statement using logical operators like and, or, and not. These operators are useful for handling more complex conditions.
a) Using and Operator
The and operator returns True if both conditions are true.
Example:
age = 30
has_id_card = True
if age >= 18 and has_id_card:
print("You are eligible for an adult membership.")
In this case, the membership eligibility requires both age >= 18 and has_id_card to be true.
b) Using or Operator
The or operator returns True if at least one of the conditions is true.
Example:
has_ticket = False
has_invitation = True
if has_ticket or has_invitation:
print("You are allowed to enter the event.")
In this case, the person is allowed to enter the event if they have either a ticket or an invitation.
c) Using not Operator
The not operator negates the condition, making True become False and vice versa.
Example:
is_sunny = False
if not is_sunny:
print("It might rain today.")
In this case, not is_sunny turns the condition to True, and "It might rain today." is printed.
6. The if-else and if-elif-else Statements
a) if-else Statement
The if-else statement is used when you have two options, one to execute if the condition is True, and one to execute if the condition is False.
Syntax:
if condition:
# Code to execute if condition is True
else:
# Code to execute if condition is False
Example:
temperature = 35
if temperature > 30:
print("It's a hot day.")
else:
print("It's a cool day.")
b) if-elif-else Statement
The if-elif-else statement is used when you have multiple conditions to check. It allows you to check several conditions and execute the corresponding block of code.
Syntax:
if condition1:
# Code to execute if condition1 is True
elif condition2:
# Code to execute if condition2 is True
else:
# Code to execute if neither condition1 nor condition2 is True
Example:
age = 70
if age < 18:
print("You are a minor.")
elif age < 65:
print("You are an adult.")
else:
print("You are a senior citizen.")
Here, the program checks if the person is a minor, an adult, or a senior citizen, based on their age.
7. Common Pitfalls with if Statements
- Indentation Errors: Python relies on indentation to define code blocks. Ensure your
ifstatement and its associated block are properly indented. - Missed
elseorelif: If you want to handle all cases, ensure you useelseorelifto catch the conditions that aren’t covered by theifblock. - Confusing Conditions: Make sure your conditions are clear and precise. Using the wrong comparison operator (
>vs>=) could lead to errors in logic.
8. Mini-Project: Even or Odd Number Checker
Let’s create a program that checks if a number entered by the user is even or odd.
Objective: The program will ask the user to input a number and print whether it is even or odd.
def check_even_odd():
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number % 2 == 0:
print(f"{number} is an even number.")
else:
print(f"{number} is an odd number.")
check_even_odd()
Sample Output:
Enter a number: 7
7 is an odd number.
Interview Questions and Answers
Q: What is the output of the following code?
x = 5
if x == 5:
print("Equal")
else:
print("Not Equal")
A: The output will be "Equal".
Amazon
Q: Can you have an if statement without an else or elif?
A: Yes, you can have an if statement without else or elif. The else and elif parts are optional.
TCS
Q: What will happen if the if condition is always False?
A: If the condition is always False, the code inside the if block will never execute, and the program will skip it.
Infosys
Q: How can we use if statements to check for multiple conditions in Python?
A: You can use logical operators like and, or, and not to check multiple conditions in a single if statement.
Zoho
Q: How do you write a conditional statement to check if a number is positive, negative, or zero?
A:
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number > 0:
print("Positive")
elif number < 0:
print("Negative")
else:
print("Zero")
Conclusion
The if statement is a fundamental concept in Python that allows you to make decisions and control the flow of your program based on conditions. By using the if, elif, and else statements, along with logical operators, you can handle complex decision-making scenarios. Mastering the if statement is crucial for writing dynamic, responsive Python programs.
If statement
Question
Your answer:
Correct answer:
Your Answers
