Introduction to Queues
Queues in C are a linear data structure that follow the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. This means that elements are added at one end (rear) and removed from the other end (front). Queues are widely used in real-world scenarios such as task scheduling, data buffering, and breadth-first search algorithms.
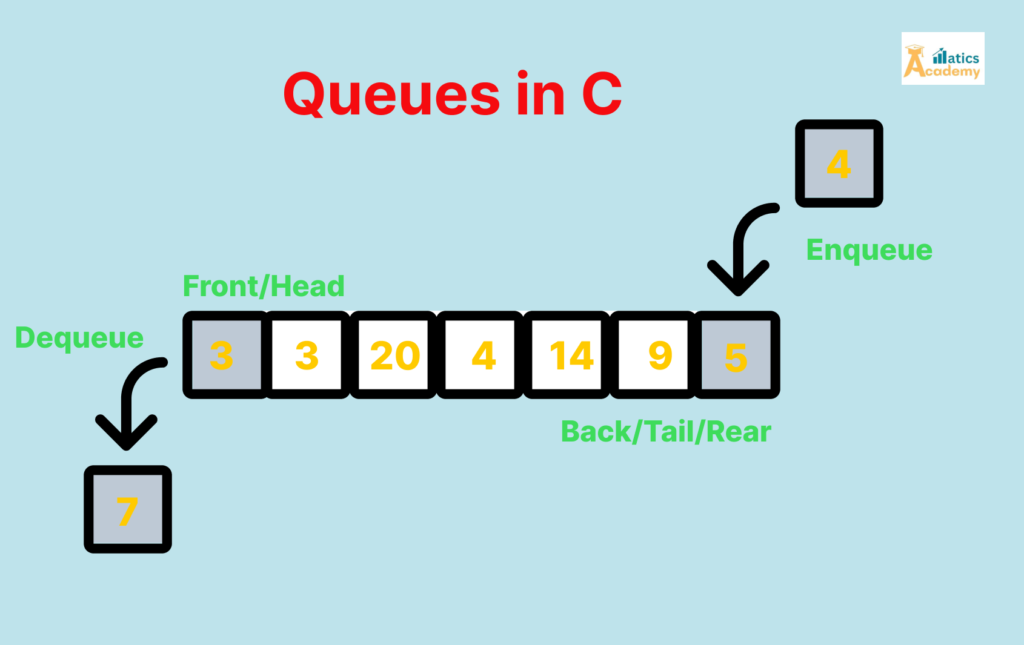
Key Features of Queues
- FIFO Mechanism: The first element added is the first to be removed.
- Two Main Operations:
- Enqueue: Adding an element to the rear.
- Dequeue: Removing an element from the front.
- Fixed or Dynamic Size: Can be implemented using arrays or linked lists.
Types of Queues in C
- Simple Queue
Follows the basic FIFO principle. - Circular Queue
The rear wraps around to the front when the queue reaches the end. - Priority Queue
Elements are dequeued based on priority rather than the order of insertion. - Double-Ended Queue (Deque)
Allows insertion and deletion at both ends.
Implementing a Simple Queues in C Using Arrays
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 5
int queue[SIZE];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
// Function to add an element to the queue
void enqueue(int value) {
if (rear == SIZE - 1) {
printf("Queue Overflow\n");
return;
}
if (front == -1) {
front = 0;
}
queue[++rear] = value;
printf("%d enqueued to queue\n", value);
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
void dequeue() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
printf("Queue Underflow\n");
return;
}
printf("%d dequeued from queue\n", queue[front++]);
}
// Function to display the queue
void display() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Queue elements are: ");
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++) {
printf("%d ", queue[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
enqueue(10);
enqueue(20);
enqueue(30);
display();
dequeue();
display();
return 0;
}
Output: Click me!
10 enqueued to queue
20 enqueued to queue
30 enqueued to queue
Queue elements are: 10 20 30
10 dequeued from queue
Queue elements are: 20 30Implementing a Circular Queues in C
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 5
int queue[SIZE];
int front = -1, rear = -1;
void enqueue(int value) {
if ((rear + 1) % SIZE == front) {
printf("Queue Overflow\n");
return;
}
if (front == -1) {
front = 0;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % SIZE;
queue[rear] = value;
printf("%d enqueued to queue\n", value);
}
void dequeue() {
if (front == -1) {
printf("Queue Underflow\n");
return;
}
printf("%d dequeued from queue\n", queue[front]);
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1; // Reset queue
} else {
front = (front + 1) % SIZE;
}
}
void display() {
if (front == -1) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Queue elements are: ");
int i = front;
while (1) {
printf("%d ", queue[i]);
if (i == rear) {
break;
}
i = (i + 1) % SIZE;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
enqueue(10);
enqueue(20);
enqueue(30);
display();
dequeue();
display();
enqueue(40);
enqueue(50);
enqueue(60); // This will trigger an overflow
display();
return 0;
}
Output: Click me!
10 enqueued to queue
20 enqueued to queue
30 enqueued to queue
Queue elements are: 10 20 30
10 dequeued from queue
Queue elements are: 20 30
40 enqueued to queue
50 enqueued to queue
Queue Overflow
Queue elements are: 20 30 40 50Operations on Queues in C
- Enqueue (Insertion)
Adds an element to the rear of the queue. - Dequeue (Deletion)
Removes an element from the front of the queue. - Peek (Front Element)
Returns the front element without removing it. - IsEmpty and IsFull
Checks if the queue is empty or full.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Efficient for managing sequential tasks.
- Dynamic implementation allows flexible memory usage.
Challenges:
- Fixed-size queues are prone to overflow.
- Requires careful management of pointers.
Best Practices of Queues in C
- Avoid Overflow and Underflow: Ensure boundary checks during enqueue and dequeue operations.
- Choose the Right Implementation: Use arrays for static queues and linked lists for dynamic queues.
- Optimize Circular Queues: For efficient use of memory.
Applications of Queues in C
- Task Scheduling: Job scheduling in operating systems.
- Data Streaming: Buffering streams of data.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): Traversing graphs or trees.
- CPU Scheduling: Managing processes in multi-tasking systems.
Conclusion
Queues in C are a versatile and essential data structure. They enable efficient task scheduling, resource management, and data processing. By mastering their implementation and understanding their various types, developers can solve complex problems effectively and optimize system performance.
Interview Questions
1. How can you implement a Queues in C using two stacks?
Company: Amazon
Answer:
- Use two stacks,
stack1andstack2. - Enqueue Operation: Push elements into
stack1. - Dequeue Operation:
- If
stack2is empty, pop all elements fromstack1and push them intostack2. - Then pop the top element from
stack2.
- If
- This method ensures the FIFO behavior of the queue using two LIFO stacks.
2. How do you implement a circular queue, and what are its advantages in Queues in C?
Company: Microsoft
Answer:
- Use an array and two indices,
frontandrear, with modular arithmetic.- Enqueue:
rear = (rear + 1) % size. - Dequeue:
front = (front + 1) % size.
- Enqueue:
- Advantages: Circular queues utilize memory efficiently by reusing empty spaces at the beginning of the array without shifting elements.
3. How would you handle queue overflow in an array-based implementation?
Company: Google
Answer:
- Dynamically resize the array when it reaches capacity:
- Allocate a new, larger array.
- Copy elements from the old array to the new array while preserving the order.
- Update
frontandrearpointers.
- Alternatively, use a linked list to avoid static size constraints.
4. What are the differences between implementing a queue with arrays and linked lists?
Company: Meta (Facebook)
Answer:
- Array-Based Queue:
- Fixed size; resizing may be required.
- Simpler implementation but wastes memory if elements are not shifted properly.
- Linked-List-Based Queue:
- Dynamic size; no resizing needed.
- Requires extra memory for pointers.
- Can easily handle overflow if memory is available.
5. Can you explain the use of priority queues in real-world applications?
Company: IBM
Answer:
- Priority queues in C assign priorities to elements, and higher-priority elements are dequeued first.
- Applications:
- Scheduling processes in operating systems (highest-priority task executed first).
- Managing patients in emergency rooms (severe cases treated first).
- Handling network traffic (important packets processed first).
Quizzes
Implementing Queues in C Quiz
