Introduction
In C programming, the main() function is the foundation of every program. It serves as the official starting point of execution, directing the flow of control throughout the application. No matter how complex or large the program is, everything begins with main(). The compiler and operating system look for this function to kick off program execution.
The importance of main() cannot be overstated—it is where the program begins, initializes operations, and often coordinates function calls and logic. Even if a program contains hundreds of other functions, none will execute unless main() runs first.
Why Study This Topic?
The main() function is not just a programming formality; it is the core command center of every C application. Whether you’re building system software, mobile applications, or embedded devices, execution starts with main(). Without a proper understanding of this function, it’s impossible to grasp how C programs operate or how to structure them effectively.
Take a real-world analogy: imagine a washing machine. You load the clothes, add detergent, and select the wash cycle. But the process doesn’t start until you press the Start button. That button triggers the internal controller to follow a sequence of actions—fill water, spin, rinse, and drain. In C programming, the main() function works just like that Start button. It tells the program to begin and manages what happens next, and in what order.
In real-world scenarios, especially in critical systems like automotive software, industrial machines, and operating systems, understanding the execution flow from main() ensures that software is structured, reliable, and predictable. It’s a fundamental concept that forms the basis of interviews, academic learning, and professional coding.
By mastering the main() function and execution flow, learners will develop the foundational mindset to write well-structured, maintainable, and efficient C programs.
What Will Be Covered?
- Definition and purpose of the
main()function - Structure and syntax
- Program execution flow
- Code examples and a flowchart
- Interview questions and answers
- Quizzes and practice coding tasks
What is the main() Function?
The main() function is the first function executed in a C program. Every standalone C application must contain exactly one main() function.
int main() {
printf("Hello, World!");
return 0;
}Real-Time Example
Think of the main() function as the engine starter in a car. No matter how advanced the car is, it won’t run until the ignition is turned on. Likewise, no part of a C program runs until the main() function is called.
Syntax of the main() Function
int main() {
// statements
return 0;
}int: Return type indicating success (0) or failure (non-zero)main(): Function name where execution begins{}: Function body containing statementsreturn 0;: Terminates the function and returns control to the operating system
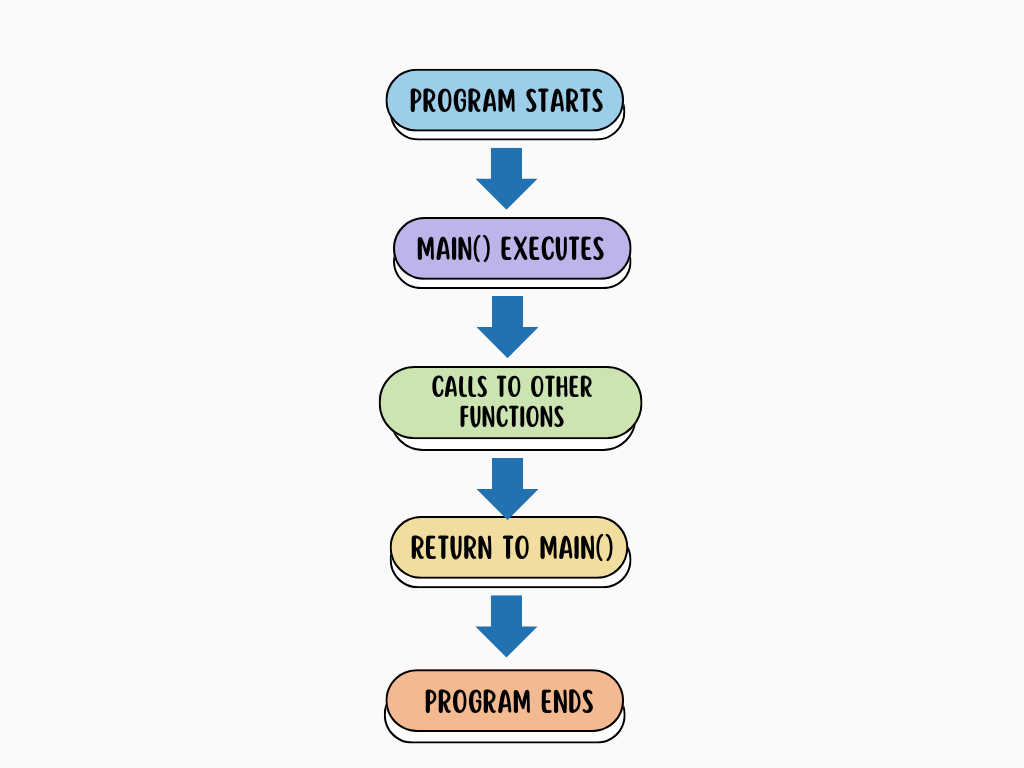
Execution Flow in C Programs
- Preprocessor Directives
- Global Declarations
main()Function Starts- Local declarations
- Executable statements
- Function calls
- User-Defined Functions (if any)
- Return to
main() - Program Ends
Flow Diagram
Summary
- The
main()function is mandatory and initiates program execution - All function calls and logic are controlled from
main() - Execution returns to
main()after any called function ends - A well-structured
main()improves modularity and readability
Learning Outcomes
After completing this topic, learners will be able to:
- Write and explain the purpose of the
main()function - Describe the flow of program execution
- Use
main()to control the logical structure of their programs
Common Interview Questions
Q1. Is the main() function mandatory in C?
A: Yes. Every C program must contain exactly one main() function.
Asked in: Infosys, TCS
Q2. What does return 0; signify in main()?
A: It indicates that the program has terminated successfully.
Asked in: Wipro, Cognizant
Q3. Can a program contain more than one main() function?
A: No. Only one main() function is allowed per program.
Asked in: Accenture, Capgemini
Q4. Is it mandatory to write return 0; in main()?
A: Most compilers insert it automatically, but it is best practice to include it.
Asked in: IBM, HCL
Q5. Can main() call other functions?
A: Yes. main() can call any number of user-defined or standard functions.
Asked in: Mindtree, Tech Mahindra
Practice Exercises
Coding Task
Write a C program that prints a welcome message, then calls another function to print your name.
Scenario
Imagine you’re running a restaurant kitchen. Nothing gets cooked until the head chef gives the go-ahead. That chef is like the main() function. All other staff (functions) depend on the chef’s instructions to begin their tasks.
Take Quiz:
Additional Resources
- Book: Programming in ANSI C by E. Balagurusamy
- Website: C Language
- Compiler: GCC
- IDEs: Code::Blocks, Dev C++, Visual Studio Code
