Overview
Method overriding in Python is a core concept of object-oriented programming that allows a subclass to redefine a method from its parent class. This technique enables developers to provide specific implementations for inherited methods, allowing runtime polymorphism and enhancing flexibility in code.
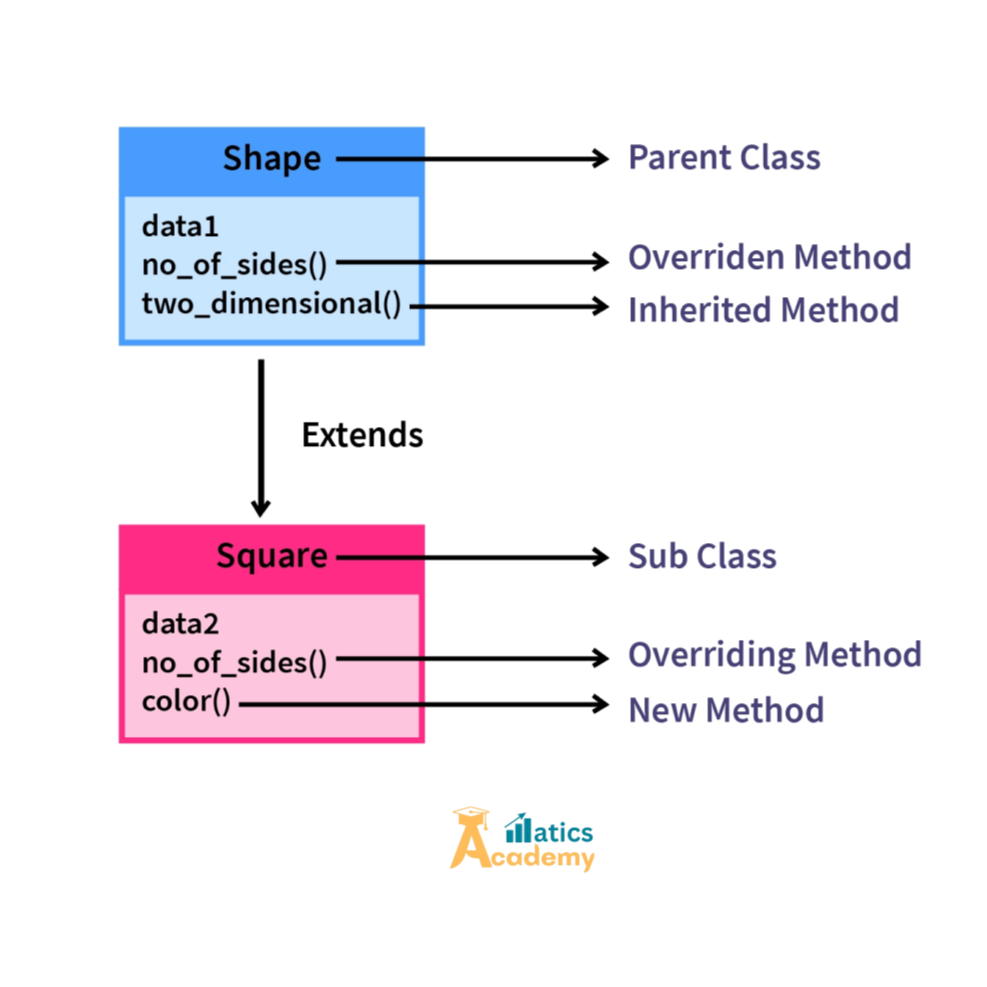
Key Features of Method Overriding
- Inheritance Requirement:
In essence, overriding occurs in a subclass, as it inherits a method from its parent class. Therefore, without inheritance, overriding is not possible. - Same Method Signature:
The name and parameters of the method in the subclass must match those in the parent class. - Runtime Polymorphism:
The decision about which method to invoke is made during runtime, based on the object type. - Flexible Behavior:
Subclasses can customize the behavior of inherited methods while retaining the same method interface.
Syntax of Method Overriding
class Parent:
def show_message(self):
print("This is the parent class method.")
class Child(Parent):
def show_message(self):
print("This is the overridden method in the child class.")
# Creating an object of the Child class
child = Child()
child.show_message()
Using super() in Method Overriding
The super() function allows access to the parent class’s method from within the overriding method in the child class. This is particularly useful when you want to retain some functionality from the parent method and extend it.
class Parent:
def show_message(self):
print("Message from the Parent class.")
class Child(Parent):
def show_message(self):
super().show_message()
print("Additional message from the Child class.")
# Example
child = Child()
child.show_message()
Examples
1.Basic Method Overriding
class Animal:
def sound(self):
print("Animals make sounds.")
class Dog(Animal):
def sound(self):
print("Dogs bark.")
dog = Dog()
dog.sound()
2.Overriding with Additional Behavior
class Employee:
def details(self):
print("Employee details.")
class Manager(Employee):
def details(self):
super().details()
print("Manager-specific details.")
manager = Manager()
manager.details()
3. Real-Life Scenario
class Shape:
def area(self):
print("Calculating area.")
class Rectangle(Shape):
def area(self):
print("Area = length * breadth.")
rect = Rectangle()
rect.area()
Advantages of Method Overriding
- Runtime Polymorphism:
As a result, different objects can provide different implementations of the same method at runtime, which enhances flexibility and adaptability in object-oriented programming. - Code Reusability:
Parent class methods can be reused with modifications in the child class. - Enhanced Flexibility:
Subclasses can tailor inherited methods to meet specific requirements.
Key Points to Remember
- The method name, parameters, and signature must match between parent and child classes.
- Overriding is only possible when the child class inherits the parent class.
- Use
super()to invoke the parent class’s method within the overridden method.
Interview Questions:
1. How does method overriding differ from overloading? (Meta)
Method overriding occurs in a subclass and involves redefining a method, whereas method overloading is defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters in the same class.
2. What is the purpose of super() in method overriding? (Microsoft)
In addition, super() is used to call the parent class’s method from the overriding method in the child class, thereby ensuring that the parent class functionality is retained.
3. Can a private method be overridden? (Amazon)
Private methods cannot be overridden because they are not accessible outside the class where they are defined. However, name mangling can provide a workaround.
