Sorting Algorithms in C is a fundamental operation in computer science that arranges elements in a specific order, usually in ascending or descending order. It is essential for efficient searching, organizing data, and optimizing other algorithms.
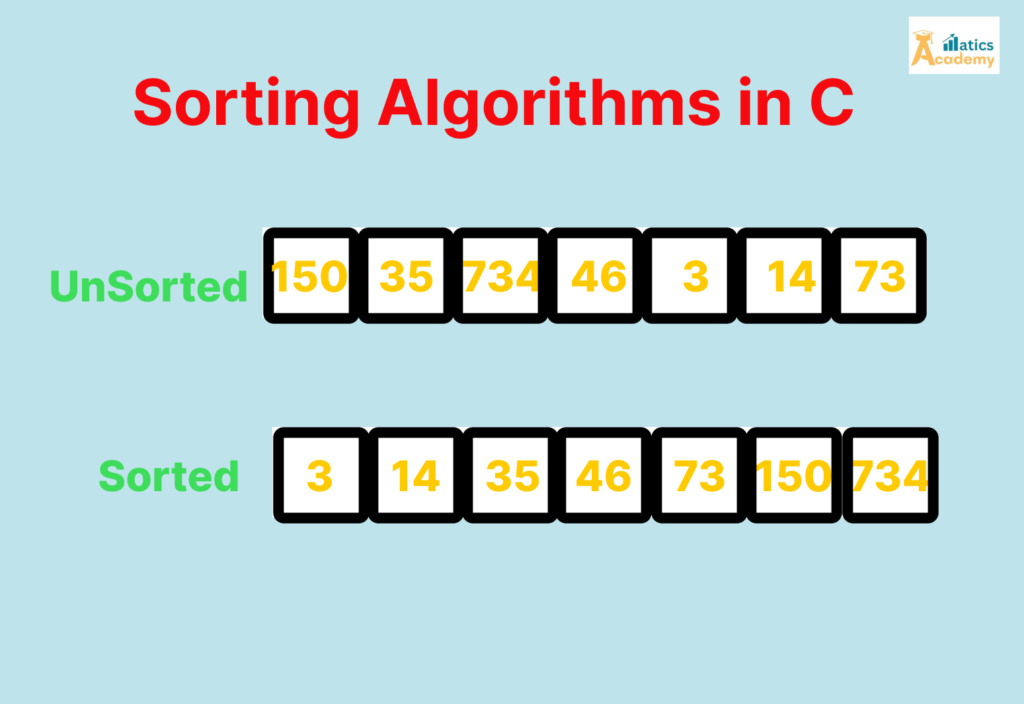
Why Sorting is Important?
Sorting plays a crucial role in various applications, including:
- Efficient Searching: Many searching algorithms, such as binary search, require sorted data.
- Data Organization: Sorted data is easier to manage and analyze.
- Improved Performance: Many algorithms work efficiently on sorted data, reducing time complexity.
- Optimization in Databases: Databases use sorting to optimize query execution.
Types of sorting Algorithms in C
1. Bubble Sort
Definition
Bubble is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. This process continues until the array is sorted.
Algorithm
- Start from the first element of the array.
- Compare it with the next element; if it’s greater, swap them.
- Move to the next pair and repeat the process.
- Repeat the above steps until the array is fully sorted.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform Bubble Sort
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 11 12 22 25 34 64 902. Selection Sort
Definition
Selection Sort in C works by repeatedly selecting the smallest element from the unsorted part of the array and swapping it with the first element of the unsorted section.
Algorithm
- Find the smallest element in the array.
- Swap it with the first element.
- Repeat for the remaining elements.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform Selection Sort
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])
minIndex = j;
}
int temp = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {29, 10, 14, 37, 13};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output: Click me!
Sorted array: 10 13 14 29 373. Insertion Sort
Definition
Insertion Sorting Algorithms in C builds the sorted array one item at a time by picking the next element and placing it in its correct position in.
Algorithm
- Start from the second element.
- Compare it with previous elements and insert it at the correct position.
- Repeat for all elements.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform Insertion Sort
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 5 6 11 12 134. Merge Sort
Definition
Merge Sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that splits the array into halves, sorts them, and then merges them back together.
Algorithm
- Divide the array into two halves.
- Recursively sort each half.
- Merge the two sorted halves.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to merge two halves
void merge(int arr[], int left, int mid, int right) {
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
int L[n1], R[n2];
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
int i = 0, j = 0, k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
} else {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
// Function to implement Merge Sort
void mergeSort(int arr[], int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, left, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
mergeSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 3 9 10 27 38 43 825. Quick Sort
Definition
Quick Sorting Algorithms in C is a divide-and-conquer sorting algorithm that selects a pivot element, partitions the array into two halves based on the pivot, and recursively sorts the two halves.
Algorithm
- Pick a pivot element (typically the last element).
- Partition the array:
- Move smaller elements to the left of the pivot.
- Move larger elements to the right.
- Recursively apply Quick Sort to the left and right partitions.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to swap two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Partition function
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
// Quick Sort function
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 1 5 7 8 9 106. Heap Sort
Definition
Heap Sort works by converting the array into a Binary Heap, extracting the maximum element, and maintaining the heap property while sorting.
Algorithm
- Build a max heap from the input array.
- Swap the largest element (root) with the last element.
- Reduce heap size and restore heap property.
- Repeat until the array is sorted.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to heapify a subtree
void heapify(int arr[], int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest])
largest = left;
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest])
largest = right;
if (largest != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
// Heap Sort function
void heapSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, n, i);
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
heapSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 5 6 7 11 12 137. Counting Sort
Definition
Counting Sorting Algorithms in C is a non-comparative sorting algorithm that sorts elements by counting the occurrences of each unique element and placing them in the correct position.
Algorithm
- Find the maximum value in the array.
- Create a count array to store the frequency of each element.
- Update the count array to store cumulative counts.
- Place the elements into the correct positions in the output array.
Implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to perform Counting Sort
void countingSort(int arr[], int n) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max)
max = arr[i];
}
int count[max + 1];
int output[n];
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++)
count[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[arr[i]]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i];
count[arr[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// Function to print array
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
countingSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output : Click me!
Sorted array: 1 2 2 3 3 4 8Conclusion
Sorting Algorithms in C are essential for organizing data efficiently. Simple algorithms like Bubble Sort and Selection Sort are easy to understand but slow, while advanced algorithms like Quick Sort and Merge Sort offer better performance. Choosing the right algorithm depends on factors like data size, stability, and efficiency. Understanding these sorting techniques helps in optimizing data processing and improving problem-solving skills.
Interview Questions
1. What is the difference between Quick Sort and Merge Sort ?
Company: Google
Answer:
- Quick Sort uses a pivot to partition the array, while Merge Sort splits the array into halves.
- Quick Sort has an average time complexity of O(n log n) but can be O(n²) in the worst case.
- Merge Sort always runs in O(n log n) time.
- Quick Sort is in-place (does not need extra space), while Merge Sort requires extra space.
2. Why is Bubble Sort not used in real-world applications?
Company: Amazon
Answer:
- Bubble Sort has a time complexity of O(n²), making it very slow for large datasets.
- It compares and swaps adjacent elements, leading to too many operations.
- More efficient algorithms like Merge Sort, Quick Sort, and Heap Sort are preferred.
3. When would you use Insertion Sort?
Company: Microsoft
Answer:
- Insertion Sort is efficient for small datasets or nearly sorted arrays.
- It has a best-case time complexity of O(n) when the array is already sorted.
- It works well when the number of elements is small (≤ 1000 elements).
4. What is the advantage of Heap Sort over Quick Sort?
Company: Meta (Facebook)
Answer:
- Heap Sort has a guaranteed O(n log n) worst-case time complexity, whereas Quick Sort can degrade to O(n²) in the worst case.
- Heap Sort does not require extra space like Merge Sort.
- However, Quick Sort is usually faster for most practical cases due to better cache performance.
5. What is a stable Sorting, and which Sorting Algorithms in C are stable?
Company: IBM
Answer:
- A stable sorting algorithm maintains the relative order of duplicate elements.
- Stable sorting algorithms: Merge Sort, Bubble Sort, and Insertion Sort.
- Unstable sorting algorithms: Quick Sort, Heap Sort, and Selection Sort.
Quizzes
Sorting Algorithms in C Quiz
